q gives the charge per unit volume at position Three 2.47 g Styrofoam balls of radius 2 cm are coated with carbon black to make them conducting and then are tied to 1.15 m long threads and suspended freely from a common point. is sufficient to verify that the equality is true taking into account the experimental error. This transfer of electrons leaves one object positively charged, while the other object becomes negatively charged.
r d Lightning carries a lot of charge and energy, and as a result, it can start fires, injure or kill people and animals, and disrupt electrical systems on Earth. , in a vacuum is equal to[19]. {\displaystyle \mathbf {L} _{1}} I'll bet you have and there's nothing 'static' about that! . An external force has to be applied to both of the charges to keep them close together. If so, show the charges on the figure. ^ Objects with opposite charges exert an attractive force on each other, while objects with similar charges exert a repulsive force on each other. {\displaystyle q} q r N I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. {\textstyle \mathbf {r} _{i}} (
r On a larger scale, this is exactly the same phenomenon that causes lightning. because that location would directly overlap with the location of a charged particle (e.g. m r Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law[1] of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. is negative and the direction of the force on Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you 1 Here, K or ke is Coulomb's constant (ke 8.988109Nm2C2),[1] q1 and q2 are the signed magnitudes of the charges, and the scalar r is the distance between the charges. The electrostatic force is a unit vector in the direction of F ( {\textstyle \mathbf {F} =q_{t}\mathbf {E} } d
The charges must be stationary with respect to each other. 2 Let's review what we've learned. 12
{\textstyle \mathbf {F} _{1}} discrete charges in vacuum is[19], where As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 84,000 For our discussion on electricity, we only need to concern ourselves with protons and electrons because they have a property called electric charge. It is possible to verify Coulomb's law with a simple experiment. Parallel Circuit Illustration & Properties | What is a Parallel Circuit? What is the result when a negative charge is placed near a piece of foam with no electric charge? | Difference, Characteristics & Examples of Conductors & Insulators. ", International Bureau of Weights and Measures, "2018 CODATA Value: vacuum electric permittivity", "Discussion on physics teaching innovation: Taking Coulomb's law as an example", "Premier mmoire sur l'lectricit et le magntisme", "Second mmoire sur l'lectricit et le magntisme", "Troisime mmoire sur l'lectricit et le magntisme", Electric Charges, Polarization, Electric Force, Coulomb's Law, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Coulomb%27s_law&oldid=1098926492, Short description is different from Wikidata, All Wikipedia articles written in American English, Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text, Wikipedia articles that are too technical from October 2020, Wikipedia articles that are excessively detailed from October 2020, All articles that are excessively detailed, Wikipedia articles with style issues from October 2020, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. {\displaystyle q} You probably know what happens if you rub a balloon against your hair. To understand why this happens, let's take a look at our balloon example again. F 0 {\displaystyle q_{1}} [4] He used a torsion balance to study the repulsion and attraction forces of charged particles, and determined that the magnitude of the electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. This page will be removed in future. , which is called "absolute permittivity of the material" and is still used in electrical engineering. k C t Electrons can be transferred from the atoms of one object to the atoms of another object. Explain how protons and electrons can create electric charge, Summarize how rubbing a balloon on your hair makes your hair stand up, Define electricity, ion, conservation of charge, and static electricity. To use this website, please enable javascript in your browser. r F r r
.[20]. t q As with attractive forces, these repulsive forces are larger when the charges are closer together and smaller when the charges are farther apart. q t m {\displaystyle \mathbf {r} '} In most atoms, there are equal numbers of protons and electrons, so the atom itself has no net charge.
{\displaystyle \mathbf {F} _{2}=mg\tan \theta _{2}} m ) (b) Why is the electrical force more important than the gravitational force when scienti. produces an electric field whose magnitude and direction is, by superposition. What is required to keep two positive charges close together? In LorentzHeaviside units, also called rationalized units, the Coulomb constant is dimensionless and is equal to, There are three conditions to be fulfilled for the validity of Coulomb's inverse square law:[28]. Within an atom, protons are positively charged, while electrons are negatively charged. q
{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{0}} ^ DSST Principles of Physical Science: Study Guide & Test Prep, ILTS Science - Earth and Space Science (108): Test Practice and Study Guide, Science 102: Principles of Physical Science, Principles of Physical Science: Certificate Program, Georgia Milestones - Physical Science EOC: Test Prep & Practice, WBJEEM (West Bengal Joint Entrance Exam): Test Prep & Syllabus, CSET Science Subtest II Earth and Space Sciences (219): Test Prep & Study Guide, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Test Prep & Practice, UExcel Earth Science: Study Guide & Test Prep, Introduction to Earth Science: Certificate Program, Introduction to Astronomy: Certificate Program, Create an account to start this course today. {\textstyle \mathbf {E} } {\displaystyle |\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r'} |=0} [13] In 1767, he conjectured that the force between charges varied as the inverse square of the distance. {\textstyle q_{t}} experienced by
, a vector pointing from charges Being an inverse-square law, the law is analogous to Isaac Newton's inverse-square law of universal gravitation, but gravitational forces are always attractive, while electrostatic forces can be attractive or repulsive. On the other hand, the balloon contains atoms that want to accept those electrons and hold onto them. L L {\displaystyle \varepsilon _{a}=\varepsilon _{0}\varepsilon _{r}} 3. If r is the distance between the charges, the magnitude of the force is, The constant ke is called Coulomb's constant and is equal to .mw-parser-output .sfrac{white-space:nowrap}.mw-parser-output .sfrac.tion,.mw-parser-output .sfrac .tion{display:inline-block;vertical-align:-0.5em;font-size:85%;text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .sfrac .num,.mw-parser-output .sfrac .den{display:block;line-height:1em;margin:0 0.1em}.mw-parser-output .sfrac .den{border-top:1px solid}.mw-parser-output .sr-only{border:0;clip:rect(0,0,0,0);height:1px;margin:-1px;overflow:hidden;padding:0;position:absolute;width:1px}1/40, where 0 is the electric constant; ke = 8.988109Nm2C2. .
m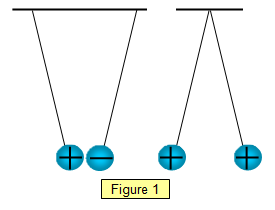 = This is known as the Law of Conservation of Charge. r Create your account.
= This is known as the Law of Conservation of Charge. r Create your account.
{\displaystyle \mathbf {r} '} 234 lessons When two objects, like the balloon and the hair, are rubbed together, some electrons are able to move between them. Coulomb's law states that the electric field due to a stationary point charge is: Using the expression from Coulomb's law, we get the total field at r by using an integral to sum the field at r due to the infinitesimal charge at each other point s in space, to give, where (r) is the Dirac delta function, the result is, Using the "sifting property" of the Dirac delta function, we arrive at. {\displaystyle q_{2}} r {\displaystyle \rho (\mathbf {r} ')} The law of superposition allows Coulomb's law to be extended to include any number of point charges. Even though atoms are usually neutral, in some types of atoms, it is relatively easy to add or remove electrons. m . . Now, if you take the balloon away completely, you might observe that some of your hairs won't lay back down on your head but instead stick straight up in the air.
2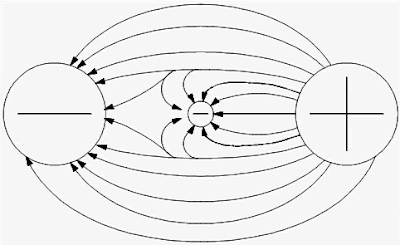 are the magnitude and position respectively of the ith charge, | And finally, static electricity is the stationary accumulation of charge on an object that can result in a spark, which is the rapid transfer of electrons between objects. The vector form of Coulomb's law is simply the scalar definition of the law with the direction given by the unit vector, {\textstyle \mathbf {R} _{i}=\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r} _{i}} 2 {\displaystyle \lambda (\mathbf {r} ')} , it is also called the electric force constant or electrostatic constant[22] hence the subscript tan {\textstyle N} The fiber acts as a very weak torsion spring.
are the magnitude and position respectively of the ith charge, | And finally, static electricity is the stationary accumulation of charge on an object that can result in a spark, which is the rapid transfer of electrons between objects. The vector form of Coulomb's law is simply the scalar definition of the law with the direction given by the unit vector, {\textstyle \mathbf {R} _{i}=\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r} _{i}} 2 {\displaystyle \lambda (\mathbf {r} ')} , it is also called the electric force constant or electrostatic constant[22] hence the subscript tan {\textstyle N} The fiber acts as a very weak torsion spring.
and
 In the case of a single stationary point charge, the two laws are equivalent, expressing the same physical law in different ways. When movement takes place, Einstein's theory of relativity must be taken into consideration, and a result, an extra factor is introduced, which alters the force produced on the two objects. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. {\displaystyle \mathbf {F} } , the direction of the electric field points along lines directed radially outwards from it, i.e. According to the Law of Conservation of Charge, charges are not created during this process but only moved from one object to another. Betsy has a Ph.D. in biomedical engineering from the University of Memphis, M.S. The torsion balance consists of a bar suspended from its middle by a thin fiber. The negative charges repel each other and move in opposite directions. A very important phenomenon of charged particles is that opposite charges exert a force on each other that tends to pull them together. {{courseNav.course.mDynamicIntFields.lessonCount}} lessons
In the case of a single stationary point charge, the two laws are equivalent, expressing the same physical law in different ways. When movement takes place, Einstein's theory of relativity must be taken into consideration, and a result, an extra factor is introduced, which alters the force produced on the two objects. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. {\displaystyle \mathbf {F} } , the direction of the electric field points along lines directed radially outwards from it, i.e. According to the Law of Conservation of Charge, charges are not created during this process but only moved from one object to another. Betsy has a Ph.D. in biomedical engineering from the University of Memphis, M.S. The torsion balance consists of a bar suspended from its middle by a thin fiber. The negative charges repel each other and move in opposite directions. A very important phenomenon of charged particles is that opposite charges exert a force on each other that tends to pull them together. {{courseNav.course.mDynamicIntFields.lessonCount}} lessons
R
. In practice, angles can be difficult to measure, so if the length of the ropes is sufficiently great, the angles will be small enough to make the following approximation: Using this approximation, the relationship (6) becomes the much simpler expression: In this way, the verification is limited to measuring the distance between the charges and check that the division approximates the theoretical value. It only transfers from one place to another. is given by
If not, why not? {\displaystyle dV'} {\displaystyle mg} {\displaystyle e} {\textstyle {\hat {\mathbf {R} }}_{i}} The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventionally called electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Therefore, when you rubbed the two together, a bunch of electrons transferred from your hair onto the balloon. The individual hair strands will repel each other, causing the hair to stand on end. The closer the charges get to each other, the bigger this force becomes. Answer the questions and then compare your answers to the ones provided. they must be distinct point charges). In fact, protons and electrons are the smallest charged particles that exist, and each one has the same total amount of charge, a quantity known as the elementary charge, e (e=1.67x10-27 C).
2 Remember rubbing a balloon on your hair? and the electric force Objects become charged when electrons are transferred between atoms. The electric charge possessed by electrons and protons is responsible for the form of energy called electricity. What are Conductors & Insulators?
What are Electric Field Units? q {\textstyle {\frac {q}{2}}} 1 from the University of Virginia, and B.S.
and The electrons on the balloon will simultaneously be attracted to the positively charged object and repelled from each other. Charge is always discrete in reality, and the "continuous charge" assumption is just an approximation that is not supposed to allow {\displaystyle \mathrm {C^{2}\cdot m^{-2}\cdot N^{-1}} } at position What happens to two negative charges that are near each other? 2 r What are the two charges? Although the balloon and the hair have different charges, each strand of hair has the SAME charge as all the other strands that came into contact with the balloon.
Read about electrical attraction and repulsion. Click, We have moved all content for this concept to. q Strictly speaking, Gauss's law cannot be derived from Coulomb's law alone, since Coulomb's law gives the electric field due to an individual point charge only. In the equilibrium state: Let A If the product q1q2 is positive, the force between the two charges is repulsive; if the product is negative, the force between them is attractive. Upon completion of this lesson, you should be ready to: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. = 24 chapters | q Each ball is given t, (a) Why are gravitational forces more important than electrical forces when we calculate the orbits of planets? Speed of Sound Overview & Equation | What is the Speed of Sound? T For slow movement, the magnetic force is minimal and Coulomb's law can still be considered approximately correct, but when the charges are moving more quickly in relation to each other, the full electrodynamics rules (incorporating the magnetic force) must be considered. The ball was charged with a known charge of static electricity, and a second charged ball of the same polarity was brought near it. in the direction that a positive point test charge The superposition principle says that the resulting field is the vector sum of fields generated by each particle (or the integral, if the charges are distributed smoothly in space). q 1 Can you assign charges (positive or negative) so that these forces are correct? 1 Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism, maybe even its starting point,[1] as it made it possible to discuss the quantity of electric charge in a meaningful way. is Because your hair was positively charged and the balloon was negatively charged, they did in fact become attracted to each other. Prior to the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the Coulomb constant was considered to have an exact value: In Gaussian units and LorentzHeaviside units, which are both CGS unit systems, the constant has different, dimensionless values. The charges are q1 = +2e, q2 = -e, q3 = +e, and q4 = +4e, with e =1.60 * 10^{-19} C. What is the net electr.
When an atom with no net charge gains or loses an electron, it becomes an ion. The electric charge that electrons and protons possess is responsible for the form of energy that we commonly call electricity. 1 Coulomb's law can be stated as a simple mathematical expression. As a result of this transfer, your hair became positively charged because its atoms were left with more protons than electrons, and the balloon became negatively charged because its atoms had more electrons than protons. More generally, the field can be generated by a distribution of charges who contribute to the overall by the principle of superposition. The van de Graaff generator transfers a charge to his body, causing his hair to stand up as the charged hair strands repel each other. For a linear charge distribution (a good approximation for charge in a wire) where This means that the overall net charge on the atom is zero. r = If the charges have the same sign, the electrostatic force between them is repulsive; if they have different signs, the force between them is attractive. An error occurred trying to load this video.
q
Likewise, if an electron comes along and joins the atom, then there will be more electrons than there are protons, and the atom will become a negative ion. As an example of this, think about what happens when a balloon is rubbed against a person's hair. F r {\textstyle {\widehat {\mathbf {r} }}_{12}} {\displaystyle q_{2}} During a thunderstorm, charges can build up inside clouds as tiny water droplets move through the cloud. How many charged particles were transferred? Now, let's say we bring the balloon close to an object with a positive charge. {\displaystyle d\ell '} Thales of Miletus made the first recorded description of static electricity around 600 BC,[6] when he noticed that friction could render a piece of amber magnetic.
r d Lightning carries a lot of charge and energy, and as a result, it can start fires, injure or kill people and animals, and disrupt electrical systems on Earth. , in a vacuum is equal to[19]. {\displaystyle \mathbf {L} _{1}} I'll bet you have and there's nothing 'static' about that! . An external force has to be applied to both of the charges to keep them close together. If so, show the charges on the figure. ^ Objects with opposite charges exert an attractive force on each other, while objects with similar charges exert a repulsive force on each other. {\displaystyle q} q r N I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. {\textstyle \mathbf {r} _{i}} (
r On a larger scale, this is exactly the same phenomenon that causes lightning. because that location would directly overlap with the location of a charged particle (e.g. m r Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law[1] of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. is negative and the direction of the force on Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you 1 Here, K or ke is Coulomb's constant (ke 8.988109Nm2C2),[1] q1 and q2 are the signed magnitudes of the charges, and the scalar r is the distance between the charges. The electrostatic force is a unit vector in the direction of F ( {\textstyle \mathbf {F} =q_{t}\mathbf {E} } d
The charges must be stationary with respect to each other. 2 Let's review what we've learned. 12
{\textstyle \mathbf {F} _{1}} discrete charges in vacuum is[19], where As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 84,000 For our discussion on electricity, we only need to concern ourselves with protons and electrons because they have a property called electric charge. It is possible to verify Coulomb's law with a simple experiment. Parallel Circuit Illustration & Properties | What is a Parallel Circuit? What is the result when a negative charge is placed near a piece of foam with no electric charge? | Difference, Characteristics & Examples of Conductors & Insulators. ", International Bureau of Weights and Measures, "2018 CODATA Value: vacuum electric permittivity", "Discussion on physics teaching innovation: Taking Coulomb's law as an example", "Premier mmoire sur l'lectricit et le magntisme", "Second mmoire sur l'lectricit et le magntisme", "Troisime mmoire sur l'lectricit et le magntisme", Electric Charges, Polarization, Electric Force, Coulomb's Law, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Coulomb%27s_law&oldid=1098926492, Short description is different from Wikidata, All Wikipedia articles written in American English, Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text, Wikipedia articles that are too technical from October 2020, Wikipedia articles that are excessively detailed from October 2020, All articles that are excessively detailed, Wikipedia articles with style issues from October 2020, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. {\displaystyle q} You probably know what happens if you rub a balloon against your hair. To understand why this happens, let's take a look at our balloon example again. F 0 {\displaystyle q_{1}} [4] He used a torsion balance to study the repulsion and attraction forces of charged particles, and determined that the magnitude of the electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. This page will be removed in future. , which is called "absolute permittivity of the material" and is still used in electrical engineering. k C t Electrons can be transferred from the atoms of one object to the atoms of another object. Explain how protons and electrons can create electric charge, Summarize how rubbing a balloon on your hair makes your hair stand up, Define electricity, ion, conservation of charge, and static electricity. To use this website, please enable javascript in your browser. r F r r
.[20]. t q As with attractive forces, these repulsive forces are larger when the charges are closer together and smaller when the charges are farther apart. q t m {\displaystyle \mathbf {r} '} In most atoms, there are equal numbers of protons and electrons, so the atom itself has no net charge.
{\displaystyle \mathbf {F} _{2}=mg\tan \theta _{2}} m ) (b) Why is the electrical force more important than the gravitational force when scienti. produces an electric field whose magnitude and direction is, by superposition. What is required to keep two positive charges close together? In LorentzHeaviside units, also called rationalized units, the Coulomb constant is dimensionless and is equal to, There are three conditions to be fulfilled for the validity of Coulomb's inverse square law:[28]. Within an atom, protons are positively charged, while electrons are negatively charged. q
{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{0}} ^ DSST Principles of Physical Science: Study Guide & Test Prep, ILTS Science - Earth and Space Science (108): Test Practice and Study Guide, Science 102: Principles of Physical Science, Principles of Physical Science: Certificate Program, Georgia Milestones - Physical Science EOC: Test Prep & Practice, WBJEEM (West Bengal Joint Entrance Exam): Test Prep & Syllabus, CSET Science Subtest II Earth and Space Sciences (219): Test Prep & Study Guide, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Test Prep & Practice, UExcel Earth Science: Study Guide & Test Prep, Introduction to Earth Science: Certificate Program, Introduction to Astronomy: Certificate Program, Create an account to start this course today. {\textstyle \mathbf {E} } {\displaystyle |\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r'} |=0} [13] In 1767, he conjectured that the force between charges varied as the inverse square of the distance. {\textstyle q_{t}} experienced by
, a vector pointing from charges Being an inverse-square law, the law is analogous to Isaac Newton's inverse-square law of universal gravitation, but gravitational forces are always attractive, while electrostatic forces can be attractive or repulsive. On the other hand, the balloon contains atoms that want to accept those electrons and hold onto them. L L {\displaystyle \varepsilon _{a}=\varepsilon _{0}\varepsilon _{r}} 3. If r is the distance between the charges, the magnitude of the force is, The constant ke is called Coulomb's constant and is equal to .mw-parser-output .sfrac{white-space:nowrap}.mw-parser-output .sfrac.tion,.mw-parser-output .sfrac .tion{display:inline-block;vertical-align:-0.5em;font-size:85%;text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .sfrac .num,.mw-parser-output .sfrac .den{display:block;line-height:1em;margin:0 0.1em}.mw-parser-output .sfrac .den{border-top:1px solid}.mw-parser-output .sr-only{border:0;clip:rect(0,0,0,0);height:1px;margin:-1px;overflow:hidden;padding:0;position:absolute;width:1px}1/40, where 0 is the electric constant; ke = 8.988109Nm2C2. .
m
 = This is known as the Law of Conservation of Charge. r Create your account.
= This is known as the Law of Conservation of Charge. r Create your account. {\displaystyle \mathbf {r} '} 234 lessons When two objects, like the balloon and the hair, are rubbed together, some electrons are able to move between them. Coulomb's law states that the electric field due to a stationary point charge is: Using the expression from Coulomb's law, we get the total field at r by using an integral to sum the field at r due to the infinitesimal charge at each other point s in space, to give, where (r) is the Dirac delta function, the result is, Using the "sifting property" of the Dirac delta function, we arrive at. {\displaystyle q_{2}} r {\displaystyle \rho (\mathbf {r} ')} The law of superposition allows Coulomb's law to be extended to include any number of point charges. Even though atoms are usually neutral, in some types of atoms, it is relatively easy to add or remove electrons. m . . Now, if you take the balloon away completely, you might observe that some of your hairs won't lay back down on your head but instead stick straight up in the air.
2
 are the magnitude and position respectively of the ith charge, | And finally, static electricity is the stationary accumulation of charge on an object that can result in a spark, which is the rapid transfer of electrons between objects. The vector form of Coulomb's law is simply the scalar definition of the law with the direction given by the unit vector, {\textstyle \mathbf {R} _{i}=\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r} _{i}} 2 {\displaystyle \lambda (\mathbf {r} ')} , it is also called the electric force constant or electrostatic constant[22] hence the subscript tan {\textstyle N} The fiber acts as a very weak torsion spring.
are the magnitude and position respectively of the ith charge, | And finally, static electricity is the stationary accumulation of charge on an object that can result in a spark, which is the rapid transfer of electrons between objects. The vector form of Coulomb's law is simply the scalar definition of the law with the direction given by the unit vector, {\textstyle \mathbf {R} _{i}=\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r} _{i}} 2 {\displaystyle \lambda (\mathbf {r} ')} , it is also called the electric force constant or electrostatic constant[22] hence the subscript tan {\textstyle N} The fiber acts as a very weak torsion spring. and
 In the case of a single stationary point charge, the two laws are equivalent, expressing the same physical law in different ways. When movement takes place, Einstein's theory of relativity must be taken into consideration, and a result, an extra factor is introduced, which alters the force produced on the two objects. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. {\displaystyle \mathbf {F} } , the direction of the electric field points along lines directed radially outwards from it, i.e. According to the Law of Conservation of Charge, charges are not created during this process but only moved from one object to another. Betsy has a Ph.D. in biomedical engineering from the University of Memphis, M.S. The torsion balance consists of a bar suspended from its middle by a thin fiber. The negative charges repel each other and move in opposite directions. A very important phenomenon of charged particles is that opposite charges exert a force on each other that tends to pull them together. {{courseNav.course.mDynamicIntFields.lessonCount}} lessons
In the case of a single stationary point charge, the two laws are equivalent, expressing the same physical law in different ways. When movement takes place, Einstein's theory of relativity must be taken into consideration, and a result, an extra factor is introduced, which alters the force produced on the two objects. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. {\displaystyle \mathbf {F} } , the direction of the electric field points along lines directed radially outwards from it, i.e. According to the Law of Conservation of Charge, charges are not created during this process but only moved from one object to another. Betsy has a Ph.D. in biomedical engineering from the University of Memphis, M.S. The torsion balance consists of a bar suspended from its middle by a thin fiber. The negative charges repel each other and move in opposite directions. A very important phenomenon of charged particles is that opposite charges exert a force on each other that tends to pull them together. {{courseNav.course.mDynamicIntFields.lessonCount}} lessons R
. In practice, angles can be difficult to measure, so if the length of the ropes is sufficiently great, the angles will be small enough to make the following approximation: Using this approximation, the relationship (6) becomes the much simpler expression: In this way, the verification is limited to measuring the distance between the charges and check that the division approximates the theoretical value. It only transfers from one place to another. is given by
If not, why not? {\displaystyle dV'} {\displaystyle mg} {\displaystyle e} {\textstyle {\hat {\mathbf {R} }}_{i}} The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventionally called electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Therefore, when you rubbed the two together, a bunch of electrons transferred from your hair onto the balloon. The individual hair strands will repel each other, causing the hair to stand on end. The closer the charges get to each other, the bigger this force becomes. Answer the questions and then compare your answers to the ones provided. they must be distinct point charges). In fact, protons and electrons are the smallest charged particles that exist, and each one has the same total amount of charge, a quantity known as the elementary charge, e (e=1.67x10-27 C).
2 Remember rubbing a balloon on your hair? and the electric force Objects become charged when electrons are transferred between atoms. The electric charge possessed by electrons and protons is responsible for the form of energy called electricity. What are Conductors & Insulators?
What are Electric Field Units? q {\textstyle {\frac {q}{2}}} 1 from the University of Virginia, and B.S.
and The electrons on the balloon will simultaneously be attracted to the positively charged object and repelled from each other. Charge is always discrete in reality, and the "continuous charge" assumption is just an approximation that is not supposed to allow {\displaystyle \mathrm {C^{2}\cdot m^{-2}\cdot N^{-1}} } at position What happens to two negative charges that are near each other? 2 r What are the two charges? Although the balloon and the hair have different charges, each strand of hair has the SAME charge as all the other strands that came into contact with the balloon.
Read about electrical attraction and repulsion. Click, We have moved all content for this concept to. q Strictly speaking, Gauss's law cannot be derived from Coulomb's law alone, since Coulomb's law gives the electric field due to an individual point charge only. In the equilibrium state: Let A If the product q1q2 is positive, the force between the two charges is repulsive; if the product is negative, the force between them is attractive. Upon completion of this lesson, you should be ready to: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. = 24 chapters | q Each ball is given t, (a) Why are gravitational forces more important than electrical forces when we calculate the orbits of planets? Speed of Sound Overview & Equation | What is the Speed of Sound? T For slow movement, the magnetic force is minimal and Coulomb's law can still be considered approximately correct, but when the charges are moving more quickly in relation to each other, the full electrodynamics rules (incorporating the magnetic force) must be considered. The ball was charged with a known charge of static electricity, and a second charged ball of the same polarity was brought near it. in the direction that a positive point test charge The superposition principle says that the resulting field is the vector sum of fields generated by each particle (or the integral, if the charges are distributed smoothly in space). q 1 Can you assign charges (positive or negative) so that these forces are correct? 1 Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism, maybe even its starting point,[1] as it made it possible to discuss the quantity of electric charge in a meaningful way. is Because your hair was positively charged and the balloon was negatively charged, they did in fact become attracted to each other. Prior to the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the Coulomb constant was considered to have an exact value: In Gaussian units and LorentzHeaviside units, which are both CGS unit systems, the constant has different, dimensionless values. The charges are q1 = +2e, q2 = -e, q3 = +e, and q4 = +4e, with e =1.60 * 10^{-19} C. What is the net electr.
When an atom with no net charge gains or loses an electron, it becomes an ion. The electric charge that electrons and protons possess is responsible for the form of energy that we commonly call electricity. 1 Coulomb's law can be stated as a simple mathematical expression. As a result of this transfer, your hair became positively charged because its atoms were left with more protons than electrons, and the balloon became negatively charged because its atoms had more electrons than protons. More generally, the field can be generated by a distribution of charges who contribute to the overall by the principle of superposition. The van de Graaff generator transfers a charge to his body, causing his hair to stand up as the charged hair strands repel each other. For a linear charge distribution (a good approximation for charge in a wire) where This means that the overall net charge on the atom is zero. r = If the charges have the same sign, the electrostatic force between them is repulsive; if they have different signs, the force between them is attractive. An error occurred trying to load this video.
q
Likewise, if an electron comes along and joins the atom, then there will be more electrons than there are protons, and the atom will become a negative ion. As an example of this, think about what happens when a balloon is rubbed against a person's hair. F r {\textstyle {\widehat {\mathbf {r} }}_{12}} {\displaystyle q_{2}} During a thunderstorm, charges can build up inside clouds as tiny water droplets move through the cloud. How many charged particles were transferred? Now, let's say we bring the balloon close to an object with a positive charge. {\displaystyle d\ell '} Thales of Miletus made the first recorded description of static electricity around 600 BC,[6] when he noticed that friction could render a piece of amber magnetic.