The classification system commonly used today is based on the Linnean system and has eight levels of taxa; from the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. The classification of humans is given in the chart as an example. Genus is a way to describe the generic name for an organism.
A major change to the Linnaean system was the addition of a new taxon called the domain. Dichotomous keys are usually represented in one of two ways: 1. Taxonomists classify organisms into a structural hierarchya multi-level system in which each group is nested, or contained, within a larger group. Dichotomous Key To help identify an unknown organism, you could use a tool called a dichotomous key. Each of these groups would contain still smaller groups; for example, the tree group might be divided into conifers and broadleaf trees. The order ranks below the class and above the family in the taxonomic hierarchy. The species of an organism determines the second part of its two-part name. Aristotle seems to have been a keen naturalist and studied hundreds of species during his stay on the island of Lesbos.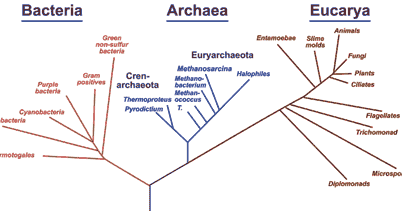 His results were far enough ahead of his time, that the principle lasted for about 2,000 years. In the same way, having two names uniquely identifies a species. *Next Generation Science Standards is a trademark of Achieve, Inc.a non-profit dedicated to raising academic standards & graduation rates. Instead, nomenclature, the scientific names given to new and old creatures, draws its inspiration from almost all languages and then 'latinizes' the word(s) to make them sound as if they could be latin.
His results were far enough ahead of his time, that the principle lasted for about 2,000 years. In the same way, having two names uniquely identifies a species. *Next Generation Science Standards is a trademark of Achieve, Inc.a non-profit dedicated to raising academic standards & graduation rates. Instead, nomenclature, the scientific names given to new and old creatures, draws its inspiration from almost all languages and then 'latinizes' the word(s) to make them sound as if they could be latin.
Such a close resemblence between the DNA of the two species suggests that humans and chimpanzees should occupy either the same, or very closely related groups in any classification scheme. All life can be sorted into three large groups called domains. Classification also helps us understand how living things are related to each other. Cancel anytime in 1-click on the manage account page before the trial ends and you won't be charged. Each phylum is divided into classes, each class into orders, each order into families, and each family into genera (genus, singular). The modern taxonomic system was developed by a Swedish Botanist, Carolus Linnaeus. The phylum (plural, phyla) ranks below the kingdom and above the class in taxonomy. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Therefore, they were classified based on the similarities in their characteristics. Latin was used not only to name creatures but also to write science papers and even letters! The domain is the highest level of organization and is the largest group. We need scientific names because every language has a different name for the same organism. Taxonomy, therefore, is the "law of arranging things" or the methods and principles of arranging the many diverse kinds of plants and animals into appropriate sets or groups. For example, members of the Phylum Arthropoda have external skeletons, segmented bodies, and jointed legs. WHAT IS THE CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS?. 2. By continuing you agree to the use of cookies. These classifications have a number of advantages. You have to choose which of the two statements best describes the unknown organism. They are, from the most to the least inclusive: Kingdoms is the most basic classification of living things. However, foxes and coyotes belong to the family Canidae. The word dinosaur means terrible lizard in Greek. Just like you, scientists group similar organisms together. In this section, find out everything you need to know about visiting the Australian Museum, how to get here and the extraordinary exhibitions on display. To help identify an unknown organism, you could use a tool called a dichotomous key. Linnaeus followed this general rule, dividing all living things into two kingdomsthe Kingdom Plantae (plants) and the Kingdom Animalia (animals). Organisms are grouped into a species based on physical and genetic similarities. Check out the What's On calendar of events, workshops and school holiday programs. Both Bacteria and Archaea consist of single-celled prokaryotes. For example, foxes, coyotes, lions, cats, otters, and weasels all belong to the Order Carnivora. You have to choose which of the two statements best describes the unknown organism. To make it easier for all scientists to do, a classification system had to be developed. Species are as specific as you can get. Sort pictures of spiders into these three groups and investigate the differences between spider species. The cat family, Felidae, includes lions, tigers, ocelots, domestic cats, bobcats, and lynx. The main criteria for an organism to be placed in a particular species is the ability to breed with other organisms of that same species. But trying to determine what kind of amphibian it is requires you to learn about taxonomy. Organisms of a class have even more in common than those in an entire phylum.
Each group in biological classificationthat is, each level in the hierarchyis called a taxon (plural, taxa).The most basic taxon is the species, a group of closely related organisms that can breed and produce offspring that in turn can reproduce. The Linnaean system is based on similarities in obvious physical traits. This phenetic method has its attractions, but even its most ardent supporters recognise that unweighted data can give rise to some unacceptable results, particularly where convergent evolution has given rise to two organisms that have totally different origins, but now look alike because they utilize the same ecological habitat. Woese further proposed a major change in classification by placing all organisms into three domainsEukarya, Bacteria, and Archaeato reflect their three separate lines of evolution. Copyright 1966 The Nuclear Science Foundation within the University of Sydney, NSW, Australia. It is rather exceptional to find only one species in a genus. Using scientific names helps scientists avoid the confusion that can arise when referring to an organism by its common, or everyday, name. Taxonomy and systematics comprise the describing, naming and classifying of plants and animals, and studying their origins and interrelationships. The genus classification is very specific so there are fewer organisms within each one. These groups are divided into smaller groups of similar organisms. Like all taxonomists, however, he was imediately faced with a problem; on what basic principle should the arrangements of groups be founded. It tells us about the inter-relationship among the various organisms. Thusthough the red fox is related to wolves, coyotes, dogs, and jackals it is less closely related to them than they are to each other. The same safe and trusted content for explorers of all ages. In addition to identifying each different kind of organism, classification can help us understand how living things are related to each other. Thank you for reading. Groups at the highest level are the largest and most general and contain a wide variety of living things. For example, Linneaus classified fungi and algae in the plant kingdom. However, no matter where you live or what language you speak, the scientific name for cat is Felis catus. The kingdom is the largest and most inclusive grouping. A single, short scientific name for each species avoids a lot of mistakes and confusion. Larger groups or groups of groups are also often written in latin (Animalia for the Animal Kingdom), and consist of one capitalized word. Eukaryota consists of all eukaryotes, from single-celled protists to humans.
By Clicking "Create Account" you agree to our Terms & Privacy policies. The lions scientific name is Panthera leo, whereas the scientific name of the tiger is Panthera tigris. For example, the human species is named Homo sapiens. The Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia all belong to the domain Eukarya. That 'look', out of context, is not the best way of establishing a classification relationship. Dichotomous keys are usually represented in one of two ways: Most biologists agree there are three domains of life on Earth: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota (see Figure below).
You use its obvious physical traits to decide what other group it is most like. It consists of a hierarchy of taxa, from the kingdom to the species. Then based on that choice, you move to the next set of statements, ultimately ending in the identity of the unknown. Comparing DNA has made the classification of organisms more precise. There are seven main levels of classification in the hierarchy. Classification is an important step in understanding the present diversity and past evolutionary history of life on Earth. (For a detailed description of domains and kingdoms, see Classification of Living Things in the article living things.). The genus (plural, genera) is the taxonomic rank between family and species. For example, a cat might be gato in Spain and mo in China and goyang-i in Korea. is shared under a CC BY-NC license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation. The second part of the scientific name is called the species name, and it is particular to each species in the genus. For this reason, there are a lot of different genera among both animals and plants. Scientists classify living things based on their shared traits. Insects, crabs, and arachnids are examples of arthropods. Bacteria are single-celled organisms without a nucleus. Many animals have evolved the ability to fly. Because mules are sterile, the interbreeding is not considered successful. It makes the study of different kinds of organisms much easier. There are different forms of organisms on earth, from minute bacteria to large elephants. Scientists classify living things based on their shared traits. DNA is often referred to as the blueprint of life because it contains the instructions for making a living organism. As a series of parallel statements laid out in a numbered sequence Both names are always written in italics, and the genus name is capitalized. The discoverers thought the word 'molest' (from the English word to attack) would be a good one so they chose the word, and then latinized it by adding "-us" to the end. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. The class ranks below the phylum and above the order in taxonomy. Lions and cats belong to the family Felidae; otters and weasels are part of the family Mustelidae. When the system was set up hundreds of years ago, Latin was considered to be the language of science. Dichotomous means divided into two parts, so the key gives a series of statements consisting of two choices that describe the characteristics of the unidentified organism. The species is the most fundamental unit in taxonomy and ranks at the base of the biological classification hierarchy. For example, a cat might be gato in Spain and mo in China and goyang-i in Korea. Taxonomists classify all organisms into a hierarchy, and give them standardised names, that are often Latin or Greek, or derived from other languages and even people's names.These specialised groups are collectively called the classification of living things. Every species is given a unique two-word name. Classification also helps us understand how living things are related to each other. Wolves, dogs, coyotes, and jackals are all members of the genus Canis. For example, from a huge systematic data bank the computer might be asked to compare a butterfly and a bee, and a butterfly and a pigeon. Some species include groups with such distinctive traits that they are classified as subspecies; in these cases, a subspecies name is added to the end of the species name. As new organisms are discovered that dont fit into any existing groups, a new group can be created and the system can be updated. From this tree, organisms that make up the domain Eukarya appear to have shared a more recent common ancestor with Archaea than Bacteria. In taxonomy, the family ranks below the order and above the genus.
You may use a dichotomous key to classify an animal and determine that it is an amphibian and not a lizard. For example, the DNA of Homo sapiens is 96% the same as chimpanzees, 80% the same as cows, and 60% the same as a fly! Kingdoms are the next level and are divided into phyla (phylum, singular).
Whales belong the Order Cetacea, a marine mammal order that counts porpoises and dolphins as members. Otherwise you will pay just $10 CAD/month for the service as long as your account is open. Usually written in Latin, it includes the genus name followed by the species name. Following are overviews of each taxonomic level in modern biological classification. In biology, classification is the process of arranging organisms, both living and extinct, into groups based on similar characteristics. for using English words!). Before the domain taxon was introduced during the 1990s, the kingdom ranked as the highest taxonomic level in classification. Organisms within each group are then further divided into smaller groups. Because they share so much in common, organisms of a family are said to be related to each other. The five-kingdom system was widely accepted and used for many years. Scientific names consist of the genus and species name, which are the most specific categories of taxonomy. Get 90 days free by inviting other teachers to try it too. Otherwise you will pay $10 CAD/month for the service as long as your account is open. A taxonomy key is used to determine to which order an organism belongs. Dichotomous means divided into two parts, so the key gives a series of statements consisting of two choices that describe the characteristics of the unidentified organism. Each species is given a unique two-word Latin name. Closely related species are grouped together in a genus. He grouped together organisms that shared obvious physical traits, such as number of legs or shape of leaves. Please ask your teacher to signup for you! Come and explore what our researchers, curators and education programs have to offer. Close grouping together of butterflies and pigeons would be a big mistake despite the importance of flight as a characteristic. Occasionally, when it is necessary to designate a subspecies, a third italicized, but uncapitalized name is added. Blue Butterflies are Morpho spp. It happens all the time! Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The science of naming and classifying living things into groups is called taxonomy. Why is having two names so important? The two-part scientific name is sometimes called a binomialfrom the Latin words bi-, meaning two, and nomen, meaning name. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule of inheritance found inside the nucleus of cells. All modern classification systems have their roots in the Linnaean classification system. To re-enable the tools or to convert back to English, click "view original" on the Google Translate toolbar. By convention the names are given in Latin. We need scientific names because every language has a different name for the same organism. A single, short scientific name for each species avoids a lot of mistakes and confusion. The fact that dolphins and fish look somewhat similar is because swimming through water requires a certain 'look'. Perhaps the single greatest contribution Linnaeus made to science was his method of naming species. The variety of form within the plant and animal kingdoms is so great that it is necessary to divide each into smaller groups, known as phyla and each phylum into several classes. You have reached the end of the main content. The species name is always written in lowercase and italicized. Other types of similarity, however, can be missleading. WHAT IS THE CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS? Choose a language from the menu above to view a computer-translated version of this page. Scientists thought they were the same species until a more advanced method showed them they are NOT! Aristotle chose as his 'oranizing principle' the concept of complexity. The groups of organisms in a genus share many structural similarities and are very closely related. This sounds suspiciously evolutionary, but Aristotle was not really an early evolutionist, he was just using complexity (often an evolutionary trend) as a taxanomic organizing principle. Accessible across all of today's devices: phones, tablets, and desktops. It happens all the time! A complete classification of two common species will show you how the system works. Receive the latest news on events, exhibitions, scienceresearch and specialoffers. Join us, volunteer and be a part of our journey of discovery! For example, when a new type of mosquito found the London underground, a new name was needed. Organisms within a family have more in common than with organisms in any classification level above it. What are the eight levels of organization used for classifying all living things? 15.1: How do we categorize living things? The Linnaean system of classification consists of a hierarchy of groupings, called taxa(singular, taxon). Organisms are examined from as many points of view as possible. Please note: Text within images is not translated, some features may not work properly after translation, and the translation may not accurately convey the intended meaning. A group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals that reproduce. Organizing large amounts of information in a standardized way makes it easy to locate information and to communicate it to others. Sometimes you may find two organisms that are visually identical but very different genetically, like a pill bug and a pill millipede. These physical similarities suggest that there is a common ancestry among those organisms in a particular phylum. Image credit: gadigal yilimung (shield) madeby UncleCharlesChickaMadden. School excursions at the Australian Museum, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Collection, Australian Museum Research Institute (AMRI), Australian Museum Lizard Island Research Station. It helps environmentalists to develop new methods of conservation of plants and animals. In this section, explore all the different ways you can be a part of the Museum's groundbreaking research, as well as come face-to-face with our dedicated staff. All life can be sorted into three large groups called domains. Must be a grown up to make an account. Scientists use an internationally accepted system for classifying and naming organisms. It is the lowest and most strict level of classification of living things. The recently added domain is a larger and more inclusive taxon than the kingdom. A muscular foot and a soft unsegmented body that may or may not be covered with a shell are hallmarks of the Phylum Mollusca; familiar mollusks include mussels, snails, and clams. Scientists thought they were the same species until a more advanced method showed them they are NOT! Phylum is the next level following kingdom in the classification of living things. We acknowledge Elders past, presentandemerging. All members of a species have the same number of chromosomes. Since then, many new species have been discovered. Each principle appears equally valid, so how and what do you choose? For his contribution, Linnaeus is known as the father of taxonomy. You can learn more about Linnaeus and his system of classification by watching the video at this link: http://teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?video_id=169889. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. The tree divides all organisms into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Improved homework resources designed to support a variety of curriculum subjects and standards. For example, the name robin may refer to the European robin or to the American robin, or even to any of several other birds; however the robins scientific namesErithacus rubecula and Turdus migratorius (European robin and American robin, respectively)clearly identify the species being referenced. After translating an article, all tools except font up/font down will be disabled. All living organisms are classified based on basic, shared characteristics. Systematic classification has an important place in scientific method. However, no matter where you live or what language you speak, the scientific name for cat is Felis catus.
A major change to the Linnaean system was the addition of a new taxon called the domain. Dichotomous keys are usually represented in one of two ways: 1. Taxonomists classify organisms into a structural hierarchya multi-level system in which each group is nested, or contained, within a larger group. Dichotomous Key To help identify an unknown organism, you could use a tool called a dichotomous key. Each of these groups would contain still smaller groups; for example, the tree group might be divided into conifers and broadleaf trees. The order ranks below the class and above the family in the taxonomic hierarchy. The species of an organism determines the second part of its two-part name. Aristotle seems to have been a keen naturalist and studied hundreds of species during his stay on the island of Lesbos.
 His results were far enough ahead of his time, that the principle lasted for about 2,000 years. In the same way, having two names uniquely identifies a species. *Next Generation Science Standards is a trademark of Achieve, Inc.a non-profit dedicated to raising academic standards & graduation rates. Instead, nomenclature, the scientific names given to new and old creatures, draws its inspiration from almost all languages and then 'latinizes' the word(s) to make them sound as if they could be latin.
His results were far enough ahead of his time, that the principle lasted for about 2,000 years. In the same way, having two names uniquely identifies a species. *Next Generation Science Standards is a trademark of Achieve, Inc.a non-profit dedicated to raising academic standards & graduation rates. Instead, nomenclature, the scientific names given to new and old creatures, draws its inspiration from almost all languages and then 'latinizes' the word(s) to make them sound as if they could be latin. Such a close resemblence between the DNA of the two species suggests that humans and chimpanzees should occupy either the same, or very closely related groups in any classification scheme. All life can be sorted into three large groups called domains. Classification also helps us understand how living things are related to each other. Cancel anytime in 1-click on the manage account page before the trial ends and you won't be charged. Each phylum is divided into classes, each class into orders, each order into families, and each family into genera (genus, singular). The modern taxonomic system was developed by a Swedish Botanist, Carolus Linnaeus. The phylum (plural, phyla) ranks below the kingdom and above the class in taxonomy. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Therefore, they were classified based on the similarities in their characteristics. Latin was used not only to name creatures but also to write science papers and even letters! The domain is the highest level of organization and is the largest group. We need scientific names because every language has a different name for the same organism. Taxonomy, therefore, is the "law of arranging things" or the methods and principles of arranging the many diverse kinds of plants and animals into appropriate sets or groups. For example, members of the Phylum Arthropoda have external skeletons, segmented bodies, and jointed legs. WHAT IS THE CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS?. 2. By continuing you agree to the use of cookies. These classifications have a number of advantages. You have to choose which of the two statements best describes the unknown organism. They are, from the most to the least inclusive: Kingdoms is the most basic classification of living things. However, foxes and coyotes belong to the family Canidae. The word dinosaur means terrible lizard in Greek. Just like you, scientists group similar organisms together. In this section, find out everything you need to know about visiting the Australian Museum, how to get here and the extraordinary exhibitions on display. To help identify an unknown organism, you could use a tool called a dichotomous key. Linnaeus followed this general rule, dividing all living things into two kingdomsthe Kingdom Plantae (plants) and the Kingdom Animalia (animals). Organisms are grouped into a species based on physical and genetic similarities. Check out the What's On calendar of events, workshops and school holiday programs. Both Bacteria and Archaea consist of single-celled prokaryotes. For example, foxes, coyotes, lions, cats, otters, and weasels all belong to the Order Carnivora. You have to choose which of the two statements best describes the unknown organism. To make it easier for all scientists to do, a classification system had to be developed. Species are as specific as you can get. Sort pictures of spiders into these three groups and investigate the differences between spider species. The cat family, Felidae, includes lions, tigers, ocelots, domestic cats, bobcats, and lynx. The main criteria for an organism to be placed in a particular species is the ability to breed with other organisms of that same species. But trying to determine what kind of amphibian it is requires you to learn about taxonomy. Organisms of a class have even more in common than those in an entire phylum.
Each group in biological classificationthat is, each level in the hierarchyis called a taxon (plural, taxa).The most basic taxon is the species, a group of closely related organisms that can breed and produce offspring that in turn can reproduce. The Linnaean system is based on similarities in obvious physical traits. This phenetic method has its attractions, but even its most ardent supporters recognise that unweighted data can give rise to some unacceptable results, particularly where convergent evolution has given rise to two organisms that have totally different origins, but now look alike because they utilize the same ecological habitat. Woese further proposed a major change in classification by placing all organisms into three domainsEukarya, Bacteria, and Archaeato reflect their three separate lines of evolution. Copyright 1966 The Nuclear Science Foundation within the University of Sydney, NSW, Australia. It is rather exceptional to find only one species in a genus. Using scientific names helps scientists avoid the confusion that can arise when referring to an organism by its common, or everyday, name. Taxonomy and systematics comprise the describing, naming and classifying of plants and animals, and studying their origins and interrelationships. The genus classification is very specific so there are fewer organisms within each one. These groups are divided into smaller groups of similar organisms. Like all taxonomists, however, he was imediately faced with a problem; on what basic principle should the arrangements of groups be founded. It tells us about the inter-relationship among the various organisms. Thusthough the red fox is related to wolves, coyotes, dogs, and jackals it is less closely related to them than they are to each other. The same safe and trusted content for explorers of all ages. In addition to identifying each different kind of organism, classification can help us understand how living things are related to each other. Thank you for reading. Groups at the highest level are the largest and most general and contain a wide variety of living things. For example, Linneaus classified fungi and algae in the plant kingdom. However, no matter where you live or what language you speak, the scientific name for cat is Felis catus. The kingdom is the largest and most inclusive grouping. A single, short scientific name for each species avoids a lot of mistakes and confusion. Larger groups or groups of groups are also often written in latin (Animalia for the Animal Kingdom), and consist of one capitalized word. Eukaryota consists of all eukaryotes, from single-celled protists to humans.
By Clicking "Create Account" you agree to our Terms & Privacy policies. The lions scientific name is Panthera leo, whereas the scientific name of the tiger is Panthera tigris. For example, the human species is named Homo sapiens. The Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia all belong to the domain Eukarya. That 'look', out of context, is not the best way of establishing a classification relationship. Dichotomous keys are usually represented in one of two ways: Most biologists agree there are three domains of life on Earth: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota (see Figure below).
You use its obvious physical traits to decide what other group it is most like. It consists of a hierarchy of taxa, from the kingdom to the species. Then based on that choice, you move to the next set of statements, ultimately ending in the identity of the unknown. Comparing DNA has made the classification of organisms more precise. There are seven main levels of classification in the hierarchy. Classification is an important step in understanding the present diversity and past evolutionary history of life on Earth. (For a detailed description of domains and kingdoms, see Classification of Living Things in the article living things.). The genus (plural, genera) is the taxonomic rank between family and species. For example, a cat might be gato in Spain and mo in China and goyang-i in Korea. is shared under a CC BY-NC license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation. The second part of the scientific name is called the species name, and it is particular to each species in the genus. For this reason, there are a lot of different genera among both animals and plants. Scientists classify living things based on their shared traits. Insects, crabs, and arachnids are examples of arthropods. Bacteria are single-celled organisms without a nucleus. Many animals have evolved the ability to fly. Because mules are sterile, the interbreeding is not considered successful. It makes the study of different kinds of organisms much easier. There are different forms of organisms on earth, from minute bacteria to large elephants. Scientists classify living things based on their shared traits. DNA is often referred to as the blueprint of life because it contains the instructions for making a living organism. As a series of parallel statements laid out in a numbered sequence Both names are always written in italics, and the genus name is capitalized. The discoverers thought the word 'molest' (from the English word to attack) would be a good one so they chose the word, and then latinized it by adding "-us" to the end. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. The class ranks below the phylum and above the order in taxonomy. Lions and cats belong to the family Felidae; otters and weasels are part of the family Mustelidae. When the system was set up hundreds of years ago, Latin was considered to be the language of science. Dichotomous means divided into two parts, so the key gives a series of statements consisting of two choices that describe the characteristics of the unidentified organism. The species is the most fundamental unit in taxonomy and ranks at the base of the biological classification hierarchy. For example, a cat might be gato in Spain and mo in China and goyang-i in Korea. Taxonomists classify all organisms into a hierarchy, and give them standardised names, that are often Latin or Greek, or derived from other languages and even people's names.These specialised groups are collectively called the classification of living things. Every species is given a unique two-word name. Classification also helps us understand how living things are related to each other. Wolves, dogs, coyotes, and jackals are all members of the genus Canis. For example, from a huge systematic data bank the computer might be asked to compare a butterfly and a bee, and a butterfly and a pigeon. Some species include groups with such distinctive traits that they are classified as subspecies; in these cases, a subspecies name is added to the end of the species name. As new organisms are discovered that dont fit into any existing groups, a new group can be created and the system can be updated. From this tree, organisms that make up the domain Eukarya appear to have shared a more recent common ancestor with Archaea than Bacteria. In taxonomy, the family ranks below the order and above the genus.
You may use a dichotomous key to classify an animal and determine that it is an amphibian and not a lizard. For example, the DNA of Homo sapiens is 96% the same as chimpanzees, 80% the same as cows, and 60% the same as a fly! Kingdoms are the next level and are divided into phyla (phylum, singular).
Whales belong the Order Cetacea, a marine mammal order that counts porpoises and dolphins as members. Otherwise you will pay just $10 CAD/month for the service as long as your account is open. Usually written in Latin, it includes the genus name followed by the species name. Following are overviews of each taxonomic level in modern biological classification. In biology, classification is the process of arranging organisms, both living and extinct, into groups based on similar characteristics. for using English words!). Before the domain taxon was introduced during the 1990s, the kingdom ranked as the highest taxonomic level in classification. Organisms within each group are then further divided into smaller groups. Because they share so much in common, organisms of a family are said to be related to each other. The five-kingdom system was widely accepted and used for many years. Scientific names consist of the genus and species name, which are the most specific categories of taxonomy. Get 90 days free by inviting other teachers to try it too. Otherwise you will pay $10 CAD/month for the service as long as your account is open. A taxonomy key is used to determine to which order an organism belongs. Dichotomous means divided into two parts, so the key gives a series of statements consisting of two choices that describe the characteristics of the unidentified organism. Each species is given a unique two-word Latin name. Closely related species are grouped together in a genus. He grouped together organisms that shared obvious physical traits, such as number of legs or shape of leaves. Please ask your teacher to signup for you! Come and explore what our researchers, curators and education programs have to offer. Close grouping together of butterflies and pigeons would be a big mistake despite the importance of flight as a characteristic. Occasionally, when it is necessary to designate a subspecies, a third italicized, but uncapitalized name is added. Blue Butterflies are Morpho spp. It happens all the time! Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The science of naming and classifying living things into groups is called taxonomy. Why is having two names so important? The two-part scientific name is sometimes called a binomialfrom the Latin words bi-, meaning two, and nomen, meaning name. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule of inheritance found inside the nucleus of cells. All modern classification systems have their roots in the Linnaean classification system. To re-enable the tools or to convert back to English, click "view original" on the Google Translate toolbar. By convention the names are given in Latin. We need scientific names because every language has a different name for the same organism. A single, short scientific name for each species avoids a lot of mistakes and confusion. The fact that dolphins and fish look somewhat similar is because swimming through water requires a certain 'look'. Perhaps the single greatest contribution Linnaeus made to science was his method of naming species. The variety of form within the plant and animal kingdoms is so great that it is necessary to divide each into smaller groups, known as phyla and each phylum into several classes. You have reached the end of the main content. The species name is always written in lowercase and italicized. Other types of similarity, however, can be missleading. WHAT IS THE CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS? Choose a language from the menu above to view a computer-translated version of this page. Scientists thought they were the same species until a more advanced method showed them they are NOT! Aristotle chose as his 'oranizing principle' the concept of complexity. The groups of organisms in a genus share many structural similarities and are very closely related. This sounds suspiciously evolutionary, but Aristotle was not really an early evolutionist, he was just using complexity (often an evolutionary trend) as a taxanomic organizing principle. Accessible across all of today's devices: phones, tablets, and desktops. It happens all the time! A complete classification of two common species will show you how the system works. Receive the latest news on events, exhibitions, scienceresearch and specialoffers. Join us, volunteer and be a part of our journey of discovery! For example, when a new type of mosquito found the London underground, a new name was needed. Organisms within a family have more in common than with organisms in any classification level above it. What are the eight levels of organization used for classifying all living things? 15.1: How do we categorize living things? The Linnaean system of classification consists of a hierarchy of groupings, called taxa(singular, taxon). Organisms are examined from as many points of view as possible. Please note: Text within images is not translated, some features may not work properly after translation, and the translation may not accurately convey the intended meaning. A group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals that reproduce. Organizing large amounts of information in a standardized way makes it easy to locate information and to communicate it to others. Sometimes you may find two organisms that are visually identical but very different genetically, like a pill bug and a pill millipede. These physical similarities suggest that there is a common ancestry among those organisms in a particular phylum. Image credit: gadigal yilimung (shield) madeby UncleCharlesChickaMadden. School excursions at the Australian Museum, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Collection, Australian Museum Research Institute (AMRI), Australian Museum Lizard Island Research Station. It helps environmentalists to develop new methods of conservation of plants and animals. In this section, explore all the different ways you can be a part of the Museum's groundbreaking research, as well as come face-to-face with our dedicated staff. All life can be sorted into three large groups called domains. Must be a grown up to make an account. Scientists use an internationally accepted system for classifying and naming organisms. It is the lowest and most strict level of classification of living things. The recently added domain is a larger and more inclusive taxon than the kingdom. A muscular foot and a soft unsegmented body that may or may not be covered with a shell are hallmarks of the Phylum Mollusca; familiar mollusks include mussels, snails, and clams. Scientists thought they were the same species until a more advanced method showed them they are NOT! Phylum is the next level following kingdom in the classification of living things. We acknowledge Elders past, presentandemerging. All members of a species have the same number of chromosomes. Since then, many new species have been discovered. Each principle appears equally valid, so how and what do you choose? For his contribution, Linnaeus is known as the father of taxonomy. You can learn more about Linnaeus and his system of classification by watching the video at this link: http://teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?video_id=169889. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. The tree divides all organisms into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Improved homework resources designed to support a variety of curriculum subjects and standards. For example, the name robin may refer to the European robin or to the American robin, or even to any of several other birds; however the robins scientific namesErithacus rubecula and Turdus migratorius (European robin and American robin, respectively)clearly identify the species being referenced. After translating an article, all tools except font up/font down will be disabled. All living organisms are classified based on basic, shared characteristics. Systematic classification has an important place in scientific method. However, no matter where you live or what language you speak, the scientific name for cat is Felis catus.