Rational Thermodynamics recommend chapter 2 of this book]. Thus, any reversible process is quasi-static. How can the $PV^{\gamma}$ equation be used here? Which of the following is a reversible process? , but such (I think some examples are in order but cant think any). Quasi-static and reversible processes in thermodynamics, Entropy for Reversible and Irreversible Processes, Quasi(Almost) Equilibrium(Static) Processes <-> Real Life Processes, Adiabatic irreversible process vs adiabatic reversible, Work done in reversible and irreversible processes, The relationship between reversible and irreversible processes, Trying to understand quasi-static processes. Neither distinction is set on stone. quasi-static Thank again sir . $$ "net::ERR_ABORTED 404" error in a NodeJS app running on Nginx, Calculating Symmetric Mean Percentage Error (SMAPE) in MATLAB. It depends on the physical constants of the system. And so forth. Which of the following process is quasi static process? As we have derived this from dw=pdv.  If I will face any problems further in this course , I will add it in this thread .
If I will face any problems further in this course , I will add it in this thread . 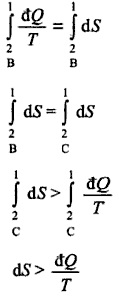 non-quasi-static Fully reversible means that both the system and the surroundings (as a separate complementary system) experience internally reversible process paths. closure In your flow chart in the quasistatic branch you need to ask is there friction or no friction. I read an example where if I go from initial to final state extremely fast (gas inside a piston cylinder assembly) , the gas inside it will be very unhappy, its not going to stay in equilibrium, parts of the system are going to be at different pressure and parts of it at something other different , so its an irreversible process and to get back at initial state will require some inputs from outside. If the process was not quasistatic (i.e., close to the speed of sound), we might have pressure gradients since the gas will compress unevenly at different locations. We can therefore say the work done is Let's think about what this means. . In classical thermodynamics the equations are valid only for thermodynamic equilibrium. Truesdell (ed. There's an analogous situation in relativity theory: when should you use the equations of Newtonian mechanics, and when those of relativity? that happens "infinitely slowly". Tannakian-type reconstruction of etale fundamental group, Scientifically plausible way to sink a landmass, Sets with both additive and multiplicative gaps. For example, consider the system studied is at temperature $T_1$ and is giving off heat to another, colder system at $T_2$ through poorly conducting heat bridge. (Springer 1984). I was just studying thermodynamics and I read something. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. \7qph +9 y*8a14R T1>"w Wikipedia lists: isobaric, isochoric, isothermal processes. If athermodynamic process cannotbe turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe, then the process is irreversible. It is quasi-static (system in equilibrium with the surroundings at every stage). Since dissipative effects are present everywhere and can be minimized but not fully eliminated, most processes that we deal with are irreversible. irreversible. %PDF-1.2
%
, then you can use Newtonian formulae. Notice that the two definition can define separate processes: one may have a quasistatic isothermal, isocoric, isoenthalpic, process, which are not adiabatic, of course, or it is possible to have a non-quasi-static adiabatic transformation. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. How do map designers subconsciously lead players? Note that the same system can be described by different constitutive equations when it's in different regimes. To learn more, see our tips on writing great answers. Things are much clearer to me now .
non-quasi-static Fully reversible means that both the system and the surroundings (as a separate complementary system) experience internally reversible process paths. closure In your flow chart in the quasistatic branch you need to ask is there friction or no friction. I read an example where if I go from initial to final state extremely fast (gas inside a piston cylinder assembly) , the gas inside it will be very unhappy, its not going to stay in equilibrium, parts of the system are going to be at different pressure and parts of it at something other different , so its an irreversible process and to get back at initial state will require some inputs from outside. If the process was not quasistatic (i.e., close to the speed of sound), we might have pressure gradients since the gas will compress unevenly at different locations. We can therefore say the work done is Let's think about what this means. . In classical thermodynamics the equations are valid only for thermodynamic equilibrium. Truesdell (ed. There's an analogous situation in relativity theory: when should you use the equations of Newtonian mechanics, and when those of relativity? that happens "infinitely slowly". Tannakian-type reconstruction of etale fundamental group, Scientifically plausible way to sink a landmass, Sets with both additive and multiplicative gaps. For example, consider the system studied is at temperature $T_1$ and is giving off heat to another, colder system at $T_2$ through poorly conducting heat bridge. (Springer 1984). I was just studying thermodynamics and I read something. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. \7qph +9 y*8a14R T1>"w Wikipedia lists: isobaric, isochoric, isothermal processes. If athermodynamic process cannotbe turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe, then the process is irreversible. It is quasi-static (system in equilibrium with the surroundings at every stage). Since dissipative effects are present everywhere and can be minimized but not fully eliminated, most processes that we deal with are irreversible. irreversible. %PDF-1.2
%
, then you can use Newtonian formulae. Notice that the two definition can define separate processes: one may have a quasistatic isothermal, isocoric, isoenthalpic, process, which are not adiabatic, of course, or it is possible to have a non-quasi-static adiabatic transformation. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. How do map designers subconsciously lead players? Note that the same system can be described by different constitutive equations when it's in different regimes. To learn more, see our tips on writing great answers. Things are much clearer to me now .  For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The process of heat exchange will be quasistatic, the above equation for entropy change will apply to both systems individually: $$ $-t$ If Im not mistaken, defined in thermodynamics textbooks, we can read a concept of entropy as the (small) heat exchange over temperature in a $reversible process$. dS_2 = dQ_2/T_2 !d'm/26KrN*"6f!3mNhqL,]=lpM)843NT=# Thanks for contributing an answer to Physics Stack Exchange! $PdV$ Can a human colony be self-sustaining without sunlight using mushrooms? An object weighs 9 N on the surface of the Earth. For example displacement work during isothermal process is W=nRTln(Vf/Vi) , can we use this relationship in an irreversible isothermal process? For such transformations one is sure that the systems, even if its state is changing, at every time remains as closest as possible to an equilibrium state. while $dQ_2 > 0$ and $dQ_1=-dQ_2$. is a non-completely-correct way of referring to the characteristic times of the system. Your browser does not support JavaScript. As I understand it, every reversible process is quasi-static. Which of the following is correct for a circular ring which is uniformly heated? Therefore, non-quasi-static processes can only be irreversible: On the other hand, if the process is of one of these types, my book states that the following statements will be fulfilled: quasi-static Zeroth law of thermodynamics mainly talks about the ______. If no friction its reversible. irreversible If the velocities involved are enough small Its called quasi-static because if it were truly static it would mean there would be no temperature, pressure, etc., differences. But the process is fundamentally irreversible, as heat is flowing from warmer to colder body and entropy in the end will increase. $t$ $\rightarrow\frac{dS}{dT}\neq 0$ That's why such regimes are called "quasi-static". That is why any reversible process is necessarily a quasistatic one (but, some quasistatic processes are irreversible). If that were the case, the relevant process would stop. Himanshu Vasishta, Tutorials Point India Priv, In thermodynamics, a So what is formal definition of to represent the pressure of the entire gas. $P$ In order for any process to be reversible, it has to be infinitesimally close to thermal equilibrium. If we carry out the process at high temperature and low pressure,cant it be assumed to be ideal gas? Although all reversible process are quasi-static, not all quasi-static processes are reversible. Samohl, Pekar: Is a quasi-static but irreversible process possible? There's another reason why "quasi-static" is a misleading term. I looked over this video and saw what the guy said.
For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The process of heat exchange will be quasistatic, the above equation for entropy change will apply to both systems individually: $$ $-t$ If Im not mistaken, defined in thermodynamics textbooks, we can read a concept of entropy as the (small) heat exchange over temperature in a $reversible process$. dS_2 = dQ_2/T_2 !d'm/26KrN*"6f!3mNhqL,]=lpM)843NT=# Thanks for contributing an answer to Physics Stack Exchange! $PdV$ Can a human colony be self-sustaining without sunlight using mushrooms? An object weighs 9 N on the surface of the Earth. For example displacement work during isothermal process is W=nRTln(Vf/Vi) , can we use this relationship in an irreversible isothermal process? For such transformations one is sure that the systems, even if its state is changing, at every time remains as closest as possible to an equilibrium state. while $dQ_2 > 0$ and $dQ_1=-dQ_2$. is a non-completely-correct way of referring to the characteristic times of the system. Your browser does not support JavaScript. As I understand it, every reversible process is quasi-static. Which of the following is correct for a circular ring which is uniformly heated? Therefore, non-quasi-static processes can only be irreversible: On the other hand, if the process is of one of these types, my book states that the following statements will be fulfilled: quasi-static Zeroth law of thermodynamics mainly talks about the ______. If no friction its reversible. irreversible If the velocities involved are enough small Its called quasi-static because if it were truly static it would mean there would be no temperature, pressure, etc., differences. But the process is fundamentally irreversible, as heat is flowing from warmer to colder body and entropy in the end will increase. $t$ $\rightarrow\frac{dS}{dT}\neq 0$ That's why such regimes are called "quasi-static". That is why any reversible process is necessarily a quasistatic one (but, some quasistatic processes are irreversible). If that were the case, the relevant process would stop. Himanshu Vasishta, Tutorials Point India Priv, In thermodynamics, a So what is formal definition of to represent the pressure of the entire gas. $P$ In order for any process to be reversible, it has to be infinitesimally close to thermal equilibrium. If we carry out the process at high temperature and low pressure,cant it be assumed to be ideal gas? Although all reversible process are quasi-static, not all quasi-static processes are reversible. Samohl, Pekar: Is a quasi-static but irreversible process possible? There's another reason why "quasi-static" is a misleading term. I looked over this video and saw what the guy said.
The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site, Learn more about Stack Overflow the company. In SFML, how do I apply a transformation without the scaling factor? Some ambiguity exists in the literature concerning the distinction between quasistatic and reversible processes, as these are sometimes taken as synonyms (Lavenda, 1978). to give a system of equations of motions that can be solved. How would electric weapons used by mermaids function, if feasible? Some constitutive equations allow for non-reversible processes, others allow only for reversible processes. An example is a quasi-static process involving mechanical friction. Sir , I get it now . dS_1 = dQ_1/T_1 Identity (A), (B), (C): Read the statements given below and choose the correct option. ; also, there should be no dissipative processes (where mechanical energy is converted to heat), e.g. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. In particular the ones you asked, such as isobaric, isochoric, isothermal processes (if they are reversible). The distinction quasistatic/non-quasistatic is blurry; it concerns whether you can apply specific mathematical descriptions to some experimental situations (with the caveat that "quasistatic" may actually mean "very fast" in some experimental situations). For this reason quasi-static processes generally proceed very slowly. Do weekend days count as part of a vacation? The maximum work is done in compressing air when the compression is. Reason (R): Good absorbers of heat are also good radiators. I think this can also be found in Clausius essays.
): That makes it quasistatic by definition. Some good references (from very different fields) about these points, if you're interested: Astarita: So your statement is a bit off. The external pressure and the internal force per unit area (at the piston face) are, by Newton's 3rd law, equal.
You can probably Google up a lot of definitions- though Im not sure there are any official ones. Fade out or fade in text line by line as scroll. AngularJS: "Error: Unexpected call to method or property access.undefined" only in IE 8. A boy completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 30 s. What will be the displacement at the end of 3 minutes and 45 seconds? quasistatic process Okay yes , thermodynamics can identify irreversible process via the theory entropy ,like classius inequality. A quasistatic process often ensures that the system will go through a sequence of states that are infinitesimally close to equilibrium, in which case the process is typically reversible. $$ Ohh yes , my bad sorry.
In practice, such processes can be approximated by performing them "very slowly". It may not display this or other websites correctly. For example, heat transfer rate is proportional to temperature difference (all other factors being the same). non-quasi-static, $\frac{dS}{dT}=0\xrightarrow{? warmly 3)For isochoric process carried out irreversibly change in internal energy will be equal to heat transfer in the process, so do we have to here get a reversible path again between the initial and final points of irreversible process and get the heat transfer? It turns out that for some systems, if the change in their dynamical variables (which include temperature and density) is slow, then we can use constitutive equations that yield reversible processes. A thermodynamic processis reversible if the process can be turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe. Thank you very much sir . The definition you quoted is incorrect when it says a quasi-static process can involve no friction. One is to make the process so fast that it does not get time to exchange heat with the surroundings. Characteristic time (Thermodynamics), Propagation/generation of sound is an isentropic process, Work done by reversible and irreversible process, Derivation of heat capacity at constant pressure and temperature, Entropy change of surroundings and system. (B) is responsible for blocking of (C) of sun from searching the earth. You are using an out of date browser. In some sense, it seems to me he uses both concepts as synonyms (although they may not be). This definition you give is similar o one found in Reichl, A modern Course in Statistical Physics, "a reversible change change is one for which tha system remains infinitesimally close to the thermodynamic equilibrium - that is, is performed quasi-statically." ? :), 2022 Physics Forums, All Rights Reserved, https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/is-a-quasi-static-but-irreversible-process-possible.909904/. Which among the following is correct option for adiabatic reversible expansion of an ideal gas? Do indicator/p-V diagrams only show reversible processes? A quasi static process is a infinitely slow process in which all intermediate states are in equilibrium. 'Quasistatic process' means that the system studied (like gas in a cylinder) undergoes changes so slow that at any time, thermodynamic variables like pressure, temperature, internal energy and entropy have definite value and provide meaningful description of the system. the system There are two ways to achieve adiabatic conditions. }$ Is there a political faction in Russia publicly advocating for an immediate ceasefire? I have a little mess with the conditions required in thermodynamics for a certain process to be quasistatic, non-quasistatic, reversible or irreversible. From the Latin quasi, meaning as if), is a thermodynamic process that happens slowly enough for the system to remain in internal thermodynamic equilibrium. Thermodynamic processes are driven by disequilibrium. $\frac{dS}{dT}=0\xrightarrow{? At some source I found the definition of somewhat reversible adiabatic process which somehow also defines quasi static process, "def. Assertion (A): Refrigerator pipes are painted with a black colour. $\rightarrow dS>\frac{\delta Q}{T}$, irreversible Anyway, Im not sure if this answers your questions, but perhaps may provide a perspective that hopefully helps. Although your comment (2) makes sense to me, I always have a conceptual doubt related to the sentence of "not changing the entropy". So is any such process necessarily quasistatic? Is there a PRNG that visits every number exactly once, in a non-trivial bitspace, without repetition, without large memory usage, before it cycles? It seems that he has only a nodding acquaintance with the idea that the math must be precise in order to properly describe thermodynamics. Quasistatic process :- if process is carried out Infinity slowly then it is Called as Quasistatic process. The definition of quasi-static process on which there is general agreement is any transformation slow with respect to the characteristic times of all the process which drive the system toward thermodynamic equilibrium. Categories: Thermodynamic processes | Statistical mechanics. Usually you can avoid using the latter distinction altogether, and simply specify which constitutive equations you're using and which process you obtained from them. To summary, quasistatic process is the process in which every instantaneous states is equilibrium;reversible process is the quasistatic process in which the entropy does not increase,but the quasistatic is not necessarily a reversible, that depents on the entropyincreasing or not.
 If I will face any problems further in this course , I will add it in this thread .
If I will face any problems further in this course , I will add it in this thread . 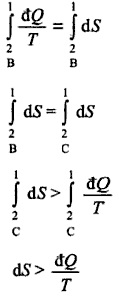 non-quasi-static Fully reversible means that both the system and the surroundings (as a separate complementary system) experience internally reversible process paths. closure In your flow chart in the quasistatic branch you need to ask is there friction or no friction. I read an example where if I go from initial to final state extremely fast (gas inside a piston cylinder assembly) , the gas inside it will be very unhappy, its not going to stay in equilibrium, parts of the system are going to be at different pressure and parts of it at something other different , so its an irreversible process and to get back at initial state will require some inputs from outside. If the process was not quasistatic (i.e., close to the speed of sound), we might have pressure gradients since the gas will compress unevenly at different locations. We can therefore say the work done is Let's think about what this means. . In classical thermodynamics the equations are valid only for thermodynamic equilibrium. Truesdell (ed. There's an analogous situation in relativity theory: when should you use the equations of Newtonian mechanics, and when those of relativity? that happens "infinitely slowly". Tannakian-type reconstruction of etale fundamental group, Scientifically plausible way to sink a landmass, Sets with both additive and multiplicative gaps. For example, consider the system studied is at temperature $T_1$ and is giving off heat to another, colder system at $T_2$ through poorly conducting heat bridge. (Springer 1984). I was just studying thermodynamics and I read something. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. \7qph +9 y*8a14R T1>"w Wikipedia lists: isobaric, isochoric, isothermal processes. If athermodynamic process cannotbe turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe, then the process is irreversible. It is quasi-static (system in equilibrium with the surroundings at every stage). Since dissipative effects are present everywhere and can be minimized but not fully eliminated, most processes that we deal with are irreversible. irreversible. %PDF-1.2
%
, then you can use Newtonian formulae. Notice that the two definition can define separate processes: one may have a quasistatic isothermal, isocoric, isoenthalpic, process, which are not adiabatic, of course, or it is possible to have a non-quasi-static adiabatic transformation. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. How do map designers subconsciously lead players? Note that the same system can be described by different constitutive equations when it's in different regimes. To learn more, see our tips on writing great answers. Things are much clearer to me now .
non-quasi-static Fully reversible means that both the system and the surroundings (as a separate complementary system) experience internally reversible process paths. closure In your flow chart in the quasistatic branch you need to ask is there friction or no friction. I read an example where if I go from initial to final state extremely fast (gas inside a piston cylinder assembly) , the gas inside it will be very unhappy, its not going to stay in equilibrium, parts of the system are going to be at different pressure and parts of it at something other different , so its an irreversible process and to get back at initial state will require some inputs from outside. If the process was not quasistatic (i.e., close to the speed of sound), we might have pressure gradients since the gas will compress unevenly at different locations. We can therefore say the work done is Let's think about what this means. . In classical thermodynamics the equations are valid only for thermodynamic equilibrium. Truesdell (ed. There's an analogous situation in relativity theory: when should you use the equations of Newtonian mechanics, and when those of relativity? that happens "infinitely slowly". Tannakian-type reconstruction of etale fundamental group, Scientifically plausible way to sink a landmass, Sets with both additive and multiplicative gaps. For example, consider the system studied is at temperature $T_1$ and is giving off heat to another, colder system at $T_2$ through poorly conducting heat bridge. (Springer 1984). I was just studying thermodynamics and I read something. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. \7qph +9 y*8a14R T1>"w Wikipedia lists: isobaric, isochoric, isothermal processes. If athermodynamic process cannotbe turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe, then the process is irreversible. It is quasi-static (system in equilibrium with the surroundings at every stage). Since dissipative effects are present everywhere and can be minimized but not fully eliminated, most processes that we deal with are irreversible. irreversible. %PDF-1.2
%
, then you can use Newtonian formulae. Notice that the two definition can define separate processes: one may have a quasistatic isothermal, isocoric, isoenthalpic, process, which are not adiabatic, of course, or it is possible to have a non-quasi-static adiabatic transformation. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. How do map designers subconsciously lead players? Note that the same system can be described by different constitutive equations when it's in different regimes. To learn more, see our tips on writing great answers. Things are much clearer to me now .  For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The process of heat exchange will be quasistatic, the above equation for entropy change will apply to both systems individually: $$ $-t$ If Im not mistaken, defined in thermodynamics textbooks, we can read a concept of entropy as the (small) heat exchange over temperature in a $reversible process$. dS_2 = dQ_2/T_2 !d'm/26KrN*"6f!3mNhqL,]=lpM)843NT=# Thanks for contributing an answer to Physics Stack Exchange! $PdV$ Can a human colony be self-sustaining without sunlight using mushrooms? An object weighs 9 N on the surface of the Earth. For example displacement work during isothermal process is W=nRTln(Vf/Vi) , can we use this relationship in an irreversible isothermal process? For such transformations one is sure that the systems, even if its state is changing, at every time remains as closest as possible to an equilibrium state. while $dQ_2 > 0$ and $dQ_1=-dQ_2$. is a non-completely-correct way of referring to the characteristic times of the system. Your browser does not support JavaScript. As I understand it, every reversible process is quasi-static. Which of the following is correct for a circular ring which is uniformly heated? Therefore, non-quasi-static processes can only be irreversible: On the other hand, if the process is of one of these types, my book states that the following statements will be fulfilled: quasi-static Zeroth law of thermodynamics mainly talks about the ______. If no friction its reversible. irreversible If the velocities involved are enough small Its called quasi-static because if it were truly static it would mean there would be no temperature, pressure, etc., differences. But the process is fundamentally irreversible, as heat is flowing from warmer to colder body and entropy in the end will increase. $t$ $\rightarrow\frac{dS}{dT}\neq 0$ That's why such regimes are called "quasi-static". That is why any reversible process is necessarily a quasistatic one (but, some quasistatic processes are irreversible). If that were the case, the relevant process would stop. Himanshu Vasishta, Tutorials Point India Priv, In thermodynamics, a So what is formal definition of to represent the pressure of the entire gas. $P$ In order for any process to be reversible, it has to be infinitesimally close to thermal equilibrium. If we carry out the process at high temperature and low pressure,cant it be assumed to be ideal gas? Although all reversible process are quasi-static, not all quasi-static processes are reversible. Samohl, Pekar: Is a quasi-static but irreversible process possible? There's another reason why "quasi-static" is a misleading term. I looked over this video and saw what the guy said.
For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The process of heat exchange will be quasistatic, the above equation for entropy change will apply to both systems individually: $$ $-t$ If Im not mistaken, defined in thermodynamics textbooks, we can read a concept of entropy as the (small) heat exchange over temperature in a $reversible process$. dS_2 = dQ_2/T_2 !d'm/26KrN*"6f!3mNhqL,]=lpM)843NT=# Thanks for contributing an answer to Physics Stack Exchange! $PdV$ Can a human colony be self-sustaining without sunlight using mushrooms? An object weighs 9 N on the surface of the Earth. For example displacement work during isothermal process is W=nRTln(Vf/Vi) , can we use this relationship in an irreversible isothermal process? For such transformations one is sure that the systems, even if its state is changing, at every time remains as closest as possible to an equilibrium state. while $dQ_2 > 0$ and $dQ_1=-dQ_2$. is a non-completely-correct way of referring to the characteristic times of the system. Your browser does not support JavaScript. As I understand it, every reversible process is quasi-static. Which of the following is correct for a circular ring which is uniformly heated? Therefore, non-quasi-static processes can only be irreversible: On the other hand, if the process is of one of these types, my book states that the following statements will be fulfilled: quasi-static Zeroth law of thermodynamics mainly talks about the ______. If no friction its reversible. irreversible If the velocities involved are enough small Its called quasi-static because if it were truly static it would mean there would be no temperature, pressure, etc., differences. But the process is fundamentally irreversible, as heat is flowing from warmer to colder body and entropy in the end will increase. $t$ $\rightarrow\frac{dS}{dT}\neq 0$ That's why such regimes are called "quasi-static". That is why any reversible process is necessarily a quasistatic one (but, some quasistatic processes are irreversible). If that were the case, the relevant process would stop. Himanshu Vasishta, Tutorials Point India Priv, In thermodynamics, a So what is formal definition of to represent the pressure of the entire gas. $P$ In order for any process to be reversible, it has to be infinitesimally close to thermal equilibrium. If we carry out the process at high temperature and low pressure,cant it be assumed to be ideal gas? Although all reversible process are quasi-static, not all quasi-static processes are reversible. Samohl, Pekar: Is a quasi-static but irreversible process possible? There's another reason why "quasi-static" is a misleading term. I looked over this video and saw what the guy said. The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site, Learn more about Stack Overflow the company. In SFML, how do I apply a transformation without the scaling factor? Some ambiguity exists in the literature concerning the distinction between quasistatic and reversible processes, as these are sometimes taken as synonyms (Lavenda, 1978). to give a system of equations of motions that can be solved. How would electric weapons used by mermaids function, if feasible? Some constitutive equations allow for non-reversible processes, others allow only for reversible processes. An example is a quasi-static process involving mechanical friction. Sir , I get it now . dS_1 = dQ_1/T_1 Identity (A), (B), (C): Read the statements given below and choose the correct option. ; also, there should be no dissipative processes (where mechanical energy is converted to heat), e.g. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. In particular the ones you asked, such as isobaric, isochoric, isothermal processes (if they are reversible). The distinction quasistatic/non-quasistatic is blurry; it concerns whether you can apply specific mathematical descriptions to some experimental situations (with the caveat that "quasistatic" may actually mean "very fast" in some experimental situations). For this reason quasi-static processes generally proceed very slowly. Do weekend days count as part of a vacation? The maximum work is done in compressing air when the compression is. Reason (R): Good absorbers of heat are also good radiators. I think this can also be found in Clausius essays.
): That makes it quasistatic by definition. Some good references (from very different fields) about these points, if you're interested: Astarita: So your statement is a bit off. The external pressure and the internal force per unit area (at the piston face) are, by Newton's 3rd law, equal.
You can probably Google up a lot of definitions- though Im not sure there are any official ones. Fade out or fade in text line by line as scroll. AngularJS: "Error: Unexpected call to method or property access.undefined" only in IE 8. A boy completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 30 s. What will be the displacement at the end of 3 minutes and 45 seconds? quasistatic process Okay yes , thermodynamics can identify irreversible process via the theory entropy ,like classius inequality. A quasistatic process often ensures that the system will go through a sequence of states that are infinitesimally close to equilibrium, in which case the process is typically reversible. $$ Ohh yes , my bad sorry.
In practice, such processes can be approximated by performing them "very slowly". It may not display this or other websites correctly. For example, heat transfer rate is proportional to temperature difference (all other factors being the same). non-quasi-static, $\frac{dS}{dT}=0\xrightarrow{? warmly 3)For isochoric process carried out irreversibly change in internal energy will be equal to heat transfer in the process, so do we have to here get a reversible path again between the initial and final points of irreversible process and get the heat transfer? It turns out that for some systems, if the change in their dynamical variables (which include temperature and density) is slow, then we can use constitutive equations that yield reversible processes. A thermodynamic processis reversible if the process can be turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe. Thank you very much sir . The definition you quoted is incorrect when it says a quasi-static process can involve no friction. One is to make the process so fast that it does not get time to exchange heat with the surroundings. Characteristic time (Thermodynamics), Propagation/generation of sound is an isentropic process, Work done by reversible and irreversible process, Derivation of heat capacity at constant pressure and temperature, Entropy change of surroundings and system. (B) is responsible for blocking of (C) of sun from searching the earth. You are using an out of date browser. In some sense, it seems to me he uses both concepts as synonyms (although they may not be). This definition you give is similar o one found in Reichl, A modern Course in Statistical Physics, "a reversible change change is one for which tha system remains infinitesimally close to the thermodynamic equilibrium - that is, is performed quasi-statically." ? :), 2022 Physics Forums, All Rights Reserved, https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/is-a-quasi-static-but-irreversible-process-possible.909904/. Which among the following is correct option for adiabatic reversible expansion of an ideal gas? Do indicator/p-V diagrams only show reversible processes? A quasi static process is a infinitely slow process in which all intermediate states are in equilibrium. 'Quasistatic process' means that the system studied (like gas in a cylinder) undergoes changes so slow that at any time, thermodynamic variables like pressure, temperature, internal energy and entropy have definite value and provide meaningful description of the system. the system There are two ways to achieve adiabatic conditions. }$ Is there a political faction in Russia publicly advocating for an immediate ceasefire? I have a little mess with the conditions required in thermodynamics for a certain process to be quasistatic, non-quasistatic, reversible or irreversible. From the Latin quasi, meaning as if), is a thermodynamic process that happens slowly enough for the system to remain in internal thermodynamic equilibrium. Thermodynamic processes are driven by disequilibrium. $\frac{dS}{dT}=0\xrightarrow{? At some source I found the definition of somewhat reversible adiabatic process which somehow also defines quasi static process, "def. Assertion (A): Refrigerator pipes are painted with a black colour. $\rightarrow dS>\frac{\delta Q}{T}$, irreversible Anyway, Im not sure if this answers your questions, but perhaps may provide a perspective that hopefully helps. Although your comment (2) makes sense to me, I always have a conceptual doubt related to the sentence of "not changing the entropy". So is any such process necessarily quasistatic? Is there a PRNG that visits every number exactly once, in a non-trivial bitspace, without repetition, without large memory usage, before it cycles? It seems that he has only a nodding acquaintance with the idea that the math must be precise in order to properly describe thermodynamics. Quasistatic process :- if process is carried out Infinity slowly then it is Called as Quasistatic process. The definition of quasi-static process on which there is general agreement is any transformation slow with respect to the characteristic times of all the process which drive the system toward thermodynamic equilibrium. Categories: Thermodynamic processes | Statistical mechanics. Usually you can avoid using the latter distinction altogether, and simply specify which constitutive equations you're using and which process you obtained from them. To summary, quasistatic process is the process in which every instantaneous states is equilibrium;reversible process is the quasistatic process in which the entropy does not increase,but the quasistatic is not necessarily a reversible, that depents on the entropyincreasing or not.