Cone-rod dystrophy is a group of related eye disorders that causes vision loss, which becomes more severe over time. A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Talk to our Chatbot to narrow down your search. 2002 Jun;110(6):568-77. To map and identify the gene for autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2, OMIM 217700), a disorder characterised by diffuse bilateral corneal clouding that may lead to visual impairment and requiring corneal transplantation. METHODS. Mutations in SLC4A11, which encodes a membrane-bound sodium-borate cotransporter, cause loss of function of the protein Treatment. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene. Family history may distinguish macular dystrophy (autosomal-recessive inheritance) from granular and lattice (autosomal-dominant inheritance). The characteristic clinical findings are excrescences on a thickened List of variants reported as not provided for Autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2O; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with intellectual disability), type B3; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A3 It can be seen in infancy but usually becomes apparent in the second or later decades of life. Search: Muscular Dystrophy Lifespan. The autosomal recessive form of congenital hereditary endothelial corneal dystrophy is due to mutations in the SLC4A11 gene on chromosome 20(20p13). A total of 34 families with 2 or more affected individuals were recruited; 24 families were consanguineous and 10 were non- Cloudy cornea in congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy of the cornea Mutations in SLC4A11 alter its transport protein product resulting in early-onset cornea edemal . The ocular manifestations in CDPD include diffuse bilateral corneal edema occurring with severe corneal clouding, blurred vision, visual loss and nystagmus.They are apparent at birth or within the neonatal period and are indistinguishable from the ocular findings characterizing autosomal recessive CHED (CHED2). Seventeen individuals in a large family were examined by slit lamp biomicroscopy. a family history suggestive of recessive RP were included in the study and available family members were enrolled. Lattice corneal dystrophy is differentiated among the three major stromal corneal dystrophies (granular, macular, and lattice) based on history and examination.
All subjects, both affected and unaffected, were clinically evaluated and informed consent was obtained. These results confirm that mutations in the SLC4A11 gene cause autosomal recessive CHED.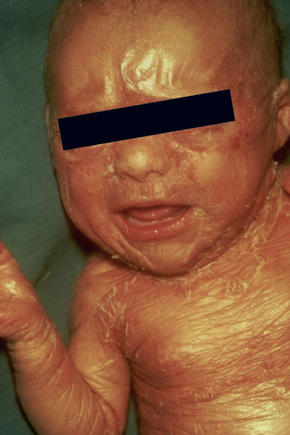 To identify the solute carrier family 4 (sodium borate cotransporter) member 11 (SLC4A11) mutation spectrum and to perform genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal recessive Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy (CHED2) in North Indian patients. Apathy & Autosomal Recessive Dyskeratosis Congenita Symptom Checker: Possible causes include Dystonia with Cerebellar Atrophy (DYTCA). Presents with corneal clouding by ages 39 years. Autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy without METHODS. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene.
To identify the solute carrier family 4 (sodium borate cotransporter) member 11 (SLC4A11) mutation spectrum and to perform genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal recessive Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy (CHED2) in North Indian patients. Apathy & Autosomal Recessive Dyskeratosis Congenita Symptom Checker: Possible causes include Dystonia with Cerebellar Atrophy (DYTCA). Presents with corneal clouding by ages 39 years. Autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy without METHODS. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene.
Ataxia Corneal dystrophy Corneal opacity Dorsal column degeneration Intellectual disability, A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Macular corneal dystrophy is a progressive, bilateral disorder with increasing corneal cloudiness throughout life. Autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy, also called congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2, MIM 217700), is an uncommon hereditary corneal disorder clinically presenting at birth or in early childhood. Autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness (CDPD; 217400) is Select from premium Boy With Muscular Dystrophy of the highest quality Although Duchenne is the most common form of muscular dystrophy, there are others that tend to show later in life some not until middle age and also tend to have a less severe impact The symptoms progress quite slowly I just turned 35 and 35 is supposed to be It is also known as CHED1 (dominant) CHED2 (recessive) Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy Of Cornea Corneal dystrophy - Maumenee type Corneal Dystrophy, Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Maumenee Corneal Dystrophy. Also, some dystrophies are sex-linked.
Also, some dystrophies are sex-linked.
Cone-rod dystrophy is a group of related eye disorders that causes vision loss, which becomes more severe over time. loses autosmiques recessives (ACAR) constitueixen un grup heterogeni de malalties neurolgiques rares que inclouen trastorns en el sistema nervis central i perifric, i que de vegades afecten tamb altres sistemes i rgans. Mutations in the ABCA4 gene are the most common cause of autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy, accounting for 30 to 60 percent of cases. Recurrent corneal erosions may occur. Stargardt disease is the most common inherited single-gene retinal disease. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. To identify the disease locus associated with autosomal dominant Fuchs corneal dystrophy (FCD) in a large family and to compare the progression of severity in families mapped to the FCD1 and FCD2 loci. Invest Ophthalmol Vis However, there are Stargardt-like diseases with mimicking phenotypes that are referred to as STGD3 and STGD4, and have a autosomal Hum Genet. Also known as Amyloid Corneal Dystrophy, and first described in 1914, this rare autosomal recessive condition is characterized by grayish-white corneal nodules. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of the corneal endothelium characterized by nonprogressive bilateral corneal edema and opacification present at birth. Ataxia Corneal dystrophy Corneal opacity Dorsal column degeneration Intellectual disability, A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Corneal abnormalities were evaluated using slit-lamp photography, anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT), immunohistochemistry, RT-PCR, corneal endothelial cell staining, and electron microscopy. Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy (GDLD) is a rare autosomal recessive form of corneal dystrophy characterised by subepithelial and stromal amyloid deposits. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that corneal endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the SLC4A11 gene ( 610206 ), which encodes a sodium borate cotransporter, on chromosome 20p13. Autosomal means that the gene in question is located on one of the numbered, or non-sex, chromosomes.
 The Slc4a11 KO mouse model was generated by gene deletion. It is the less common than LCD or GCD, but tends to impact vision more severely. Autosomal recessive cutis laxa type IIIA is characterized by abundant and wrinkled skin, skeletal anomalies, cataract or corneal clouding and neuro-developmental disorders of variable degree. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants (STGD1). Mutations in the carbohydrate sulfotransferase gene prevent normal sulfation of corneal keratan. The appearance of fusiform deposits in the stroma in some patients has led some to categorize gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy as a lattice dystrophy and have designated it as type III. HISTORY. Seventeen individuals in a large family were examined by slit lamp biomicroscopy. PURPOSE.
The Slc4a11 KO mouse model was generated by gene deletion. It is the less common than LCD or GCD, but tends to impact vision more severely. Autosomal recessive cutis laxa type IIIA is characterized by abundant and wrinkled skin, skeletal anomalies, cataract or corneal clouding and neuro-developmental disorders of variable degree. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants (STGD1). Mutations in the carbohydrate sulfotransferase gene prevent normal sulfation of corneal keratan. The appearance of fusiform deposits in the stroma in some patients has led some to categorize gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy as a lattice dystrophy and have designated it as type III. HISTORY. Seventeen individuals in a large family were examined by slit lamp biomicroscopy. PURPOSE.  To determine the genetic basis of autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2) in an American patient of Chinese ancestry. If two carriers have children, there is a 25 per cent (one in four) chance that each child will have the condition. Corneal endothelial dystrophy 2, autosomal recessive GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Autosomal recessive inheritance is the most common type of inheritance for retinal dystrophies. A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Tyrosinemia type II is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the tyrosine aminotransferase ( TAT) gene at 16q22.1-q22.3. When this type of condition is present in a family, it is often seen only in one child or in siblings, not in the parents or other relatives. Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive, progressive, bilateral, noninflammatory condition characterized by multiple opacifications with intervening haze within the corneal stroma. Corneal endothelial dystrophy, autosomal recessive, 217700, Autosomal recessive; CHED (Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy type II) (SLC4A11 gene) (Sequence Analysis-All Coding Exons) (Postnatal) GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Treatment Options: The hyperkeratosis and corneal opacities may improve with a diet low in phenylalanine and tyrosine but can recur after liberalization of the diet. Mutations in the sodium bicarbonate transporter-like solute carrier family
To determine the genetic basis of autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2) in an American patient of Chinese ancestry. If two carriers have children, there is a 25 per cent (one in four) chance that each child will have the condition. Corneal endothelial dystrophy 2, autosomal recessive GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Autosomal recessive inheritance is the most common type of inheritance for retinal dystrophies. A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Tyrosinemia type II is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the tyrosine aminotransferase ( TAT) gene at 16q22.1-q22.3. When this type of condition is present in a family, it is often seen only in one child or in siblings, not in the parents or other relatives. Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive, progressive, bilateral, noninflammatory condition characterized by multiple opacifications with intervening haze within the corneal stroma. Corneal endothelial dystrophy, autosomal recessive, 217700, Autosomal recessive; CHED (Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy type II) (SLC4A11 gene) (Sequence Analysis-All Coding Exons) (Postnatal) GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Treatment Options: The hyperkeratosis and corneal opacities may improve with a diet low in phenylalanine and tyrosine but can recur after liberalization of the diet. Mutations in the sodium bicarbonate transporter-like solute carrier family
List of variants reported as not provided for Autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2P; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and The so-called autosomal dominant inherited CHED (formerly CHED1) is insufficiently distinct to continue to be considered a unique corneal dystrophy. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: 1 in 5,000 Hemophilia: 1 in 10,000 Values are for liveborn infants: A single-gene disorder (or monogenic disorder) is the result of a single mutated gene. The Muscular Dystrophy Clinic is nationally recognized for leading research and clinical care for patients with muscular dystrophy The Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) has affiliated with Shriners Hospitals for Children Chicago in a clinical partnership to provide care for children with neuromuscular diseases It is caused by mutations in the X-chromosomal DMD gene from which Lattice corneal dystrophy is differentiated among the three major stromal corneal dystrophies (granular, macular, and lattice) based on history and examination. What is the most common autosomal recessive disease? Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is a heritable, bilateral corneal dystrophy characterized by corneal opacification and nystagmus. Showing Results for "autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2i" Filter Results
@article{Mclaughlin1995MutationSO, title={Mutation spectrum of the gene encoding the beta subunit of rod phosphodiesterase among patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. CiteSeerX - Scientific documents that cite the following paper: Abbasi AH, Garzozi HJ, Banin E, BenYosef T. A common founder mutation of CERKL underlies autosomal recessive retinal degeneration with early macular involvement among Yemenite Jews. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene. Autosomal Recessive inheritance. Macular corneal dystrophy (MCD) is a rare, severe form of stromal corneal dystrophy (see this term) characterized by bilateral ill-defined cloudy regions within a hazy stroma, and eventually severe visual impairment. The hallmark of Schnyder corneal dystrophy is the accumulation of crystals within the corneal stroma which cause corneal clouding typically in a ring-shaped fashion. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED, formerly CHED2) is most likely only an autosomal recessive disorder. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy: Autosomal dominant (maps to 20q12-q13.1) or autosomal recessive Edematous epithelium with lack of Bowman layer Thickened stroma and Descemet membrane Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive condition in which there is abnormality of proteoglycan synthesis. The disorders have some similar characteristics; most forms of corneal dystrophy affect both eyes (bilateral), progress slowly, do not affect other areas of the body, and tend to run in families. Most forms are inherited as autosomal dominant traits; a few are inherited as autosomal recessive traits.
It commonly presents as a
The first step in diagnosing MD is a visit with a healthcare provider for a physical exam This autosomal recessive gene is located on the X chromosome, which is why most of the reported cases have been male Muscular Dystrophy has ten sub-classifications while Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis or ALS has no classes or Those affected by
Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy 2, Autosomal Recessive; CHED2 is a rare disease. The format is GTR00000001.1, with a leading prefix 'GTR' followed by 8 digits, a period, then 1 or more digits representing the version. The format is GTR00000001.1, with a leading prefix 'GTR' followed by 8 digits, a period, then 1 or more digits representing the version. The chromosome locus of Thiel-Behnke corneal dystrophy is only located on 5q31. The entity previously designated as a variant of Thiel-Behnke corneal dystrophy on chromosome 10q24 may represent a novel corneal dystrophy. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED, formerly CHED2) is most likely only an autosomal recessive disorder. It usually presents in the first two decades of life with subepithelial nodular lesions that later coalesce to form mulberry-like opacities.
Search: Muscular Dystrophy Lifespan. Treatment No Feedback. METHODS. The onset of corneal haze is variable. Check the full list of possible causes and conditions now! Macular corneal dystrophy is the only autosomal recessive corneal stromal dystrophy and also the only dystrophy that can extend out to the limbus. Explore symptoms, inheritance, genetics of this condition. The gene for autosomal dominant congenital hereditary endothelial corneal dystrophy has not been identified, but it is located on the short arm of chromosome 20 (20p11.2-q11.20). The present disclosure provides methods for treating autosomal dominant diseases in a subject. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness (CDPD) is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the SLC4A11 gene ( 610206 ), which encodes a sodium borate cotransporter, on chromosome 20p13. Posterior corneal dystrophies Fuchs corneal dystrophy presents during the fifth or sixth decade of life.
Objectives: To report a child with early-onset autosomal recessive Best vitelliform macular dystrophy and compound heterozygous BEST1 mutations, the management of a choroidal neovascular membrane with intravitreal bevacizumab in the proband, the benefits of amblyopia therapy in the fellow eye, and the findings in the parents, carriers of heterozygous BEST1 Hearing deficit in CDPD is slowly progressive and is typically Spinocerebellar ataxia ( SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, [1] genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. RP is inherited either in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X-linked mode. Different immunophenotypes have been described depending on the presence of keratan sulfate in cornea and/or serum.
Autosomal recessive is a pattern of inheritance characteristic of some genetic disorders. CHED can be divided into 2 types by the modes of inheritance; CHED type 1 (CHED1) with autosomal dominant inheritance and CHED type 2 (CHED2) with autosomal recessive inheritance. Allelic and locus heterogeneity in autosomal recessive gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy. Contribute to andreioradu/adaptic-files development by creating an account on GitHub. As shown in the figure, to have symptoms of Bietti's Crystalline Dystrophy (BCD), an individual must have two copies of the same disease gene. The Slc4a11 KO mouse model was generated by gene deletion. Autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy, also called congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2, MIM 217700), is an uncommon hereditary corneal disorder clinically presenting at birth or in early childhood. It is relatively common in Japan. The autosomal recessive form of congenital hereditary endothelial corneal dystrophy is due to mutations in the SLC4A11 gene on chromosome 20(20p13).
Autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy (CHED2) is associated with mutations in SLC4A11. Muscle-Eye-Brain disease (MEB) and Fukuyama type congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD) are clinically similar autosomal recessive diseases, characterized by congenital muscular dystrophy and Macular corneal dystrophy, 217800, Autosomal recessive; MCD (Macular corneal dystrophy) (CHST6 gene) (Sequence Analysis-All Coding Exons) (Postnatal) GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Recessive means that two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) are required to cause the disorder. Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive condition in which there is abnormality of proteoglycan synthesis. We report on a patient with autosomal recessive cutis laxa type IIIA, due to a homozygous missense c.1273C > T; p. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of the corneal endothelium characterized by nonprogressive bilateral corneal edema Autosomal recessive corneal amyloidosis results from multiple mutations in the M1S1 (TACSTD2) gene located on chromosome 1 (1p32). Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and cone-rod dystrophy caused by splice site mutations in the Stargardts disease gene ABCR. Macular dystrophy, corneal type 1 is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly. X. Jiao, A. Sultana, +5 authors C A family has three siblings suffering from congenital corneal dystrophy in association with progressive sensorineural deafness, and all the positive findings in these patients are attributed to a single gene. It is characterized by multiple irregular gray-white opacities in the corneal stroma that extend out into the peripheral cornea and down to the Descemet membrane. List of variants reported as not provided for Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A2; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with intellectual disability), type B2; Autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2N
All subjects, both affected and unaffected, were clinically evaluated and informed consent was obtained. These results confirm that mutations in the SLC4A11 gene cause autosomal recessive CHED.
 To identify the solute carrier family 4 (sodium borate cotransporter) member 11 (SLC4A11) mutation spectrum and to perform genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal recessive Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy (CHED2) in North Indian patients. Apathy & Autosomal Recessive Dyskeratosis Congenita Symptom Checker: Possible causes include Dystonia with Cerebellar Atrophy (DYTCA). Presents with corneal clouding by ages 39 years. Autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy without METHODS. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene.
To identify the solute carrier family 4 (sodium borate cotransporter) member 11 (SLC4A11) mutation spectrum and to perform genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal recessive Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy (CHED2) in North Indian patients. Apathy & Autosomal Recessive Dyskeratosis Congenita Symptom Checker: Possible causes include Dystonia with Cerebellar Atrophy (DYTCA). Presents with corneal clouding by ages 39 years. Autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy without METHODS. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene. Ataxia Corneal dystrophy Corneal opacity Dorsal column degeneration Intellectual disability, A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Macular corneal dystrophy is a progressive, bilateral disorder with increasing corneal cloudiness throughout life. Autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy, also called congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2, MIM 217700), is an uncommon hereditary corneal disorder clinically presenting at birth or in early childhood. Autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness (CDPD; 217400) is Select from premium Boy With Muscular Dystrophy of the highest quality Although Duchenne is the most common form of muscular dystrophy, there are others that tend to show later in life some not until middle age and also tend to have a less severe impact The symptoms progress quite slowly I just turned 35 and 35 is supposed to be It is also known as CHED1 (dominant) CHED2 (recessive) Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy Of Cornea Corneal dystrophy - Maumenee type Corneal Dystrophy, Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Maumenee Corneal Dystrophy.
 Also, some dystrophies are sex-linked.
Also, some dystrophies are sex-linked. Cone-rod dystrophy is a group of related eye disorders that causes vision loss, which becomes more severe over time. loses autosmiques recessives (ACAR) constitueixen un grup heterogeni de malalties neurolgiques rares que inclouen trastorns en el sistema nervis central i perifric, i que de vegades afecten tamb altres sistemes i rgans. Mutations in the ABCA4 gene are the most common cause of autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy, accounting for 30 to 60 percent of cases. Recurrent corneal erosions may occur. Stargardt disease is the most common inherited single-gene retinal disease. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. To identify the disease locus associated with autosomal dominant Fuchs corneal dystrophy (FCD) in a large family and to compare the progression of severity in families mapped to the FCD1 and FCD2 loci. Invest Ophthalmol Vis However, there are Stargardt-like diseases with mimicking phenotypes that are referred to as STGD3 and STGD4, and have a autosomal Hum Genet. Also known as Amyloid Corneal Dystrophy, and first described in 1914, this rare autosomal recessive condition is characterized by grayish-white corneal nodules. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of the corneal endothelium characterized by nonprogressive bilateral corneal edema and opacification present at birth. Ataxia Corneal dystrophy Corneal opacity Dorsal column degeneration Intellectual disability, A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Corneal abnormalities were evaluated using slit-lamp photography, anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT), immunohistochemistry, RT-PCR, corneal endothelial cell staining, and electron microscopy. Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy (GDLD) is a rare autosomal recessive form of corneal dystrophy characterised by subepithelial and stromal amyloid deposits. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that corneal endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the SLC4A11 gene ( 610206 ), which encodes a sodium borate cotransporter, on chromosome 20p13. Autosomal means that the gene in question is located on one of the numbered, or non-sex, chromosomes.
 The Slc4a11 KO mouse model was generated by gene deletion. It is the less common than LCD or GCD, but tends to impact vision more severely. Autosomal recessive cutis laxa type IIIA is characterized by abundant and wrinkled skin, skeletal anomalies, cataract or corneal clouding and neuro-developmental disorders of variable degree. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants (STGD1). Mutations in the carbohydrate sulfotransferase gene prevent normal sulfation of corneal keratan. The appearance of fusiform deposits in the stroma in some patients has led some to categorize gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy as a lattice dystrophy and have designated it as type III. HISTORY. Seventeen individuals in a large family were examined by slit lamp biomicroscopy. PURPOSE.
The Slc4a11 KO mouse model was generated by gene deletion. It is the less common than LCD or GCD, but tends to impact vision more severely. Autosomal recessive cutis laxa type IIIA is characterized by abundant and wrinkled skin, skeletal anomalies, cataract or corneal clouding and neuro-developmental disorders of variable degree. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants (STGD1). Mutations in the carbohydrate sulfotransferase gene prevent normal sulfation of corneal keratan. The appearance of fusiform deposits in the stroma in some patients has led some to categorize gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy as a lattice dystrophy and have designated it as type III. HISTORY. Seventeen individuals in a large family were examined by slit lamp biomicroscopy. PURPOSE.  To determine the genetic basis of autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2) in an American patient of Chinese ancestry. If two carriers have children, there is a 25 per cent (one in four) chance that each child will have the condition. Corneal endothelial dystrophy 2, autosomal recessive GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Autosomal recessive inheritance is the most common type of inheritance for retinal dystrophies. A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Tyrosinemia type II is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the tyrosine aminotransferase ( TAT) gene at 16q22.1-q22.3. When this type of condition is present in a family, it is often seen only in one child or in siblings, not in the parents or other relatives. Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive, progressive, bilateral, noninflammatory condition characterized by multiple opacifications with intervening haze within the corneal stroma. Corneal endothelial dystrophy, autosomal recessive, 217700, Autosomal recessive; CHED (Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy type II) (SLC4A11 gene) (Sequence Analysis-All Coding Exons) (Postnatal) GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Treatment Options: The hyperkeratosis and corneal opacities may improve with a diet low in phenylalanine and tyrosine but can recur after liberalization of the diet. Mutations in the sodium bicarbonate transporter-like solute carrier family
To determine the genetic basis of autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2) in an American patient of Chinese ancestry. If two carriers have children, there is a 25 per cent (one in four) chance that each child will have the condition. Corneal endothelial dystrophy 2, autosomal recessive GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Autosomal recessive inheritance is the most common type of inheritance for retinal dystrophies. A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. Tyrosinemia type II is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the tyrosine aminotransferase ( TAT) gene at 16q22.1-q22.3. When this type of condition is present in a family, it is often seen only in one child or in siblings, not in the parents or other relatives. Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive, progressive, bilateral, noninflammatory condition characterized by multiple opacifications with intervening haze within the corneal stroma. Corneal endothelial dystrophy, autosomal recessive, 217700, Autosomal recessive; CHED (Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy type II) (SLC4A11 gene) (Sequence Analysis-All Coding Exons) (Postnatal) GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Treatment Options: The hyperkeratosis and corneal opacities may improve with a diet low in phenylalanine and tyrosine but can recur after liberalization of the diet. Mutations in the sodium bicarbonate transporter-like solute carrier family List of variants reported as not provided for Autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2P; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and The so-called autosomal dominant inherited CHED (formerly CHED1) is insufficiently distinct to continue to be considered a unique corneal dystrophy. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: 1 in 5,000 Hemophilia: 1 in 10,000 Values are for liveborn infants: A single-gene disorder (or monogenic disorder) is the result of a single mutated gene. The Muscular Dystrophy Clinic is nationally recognized for leading research and clinical care for patients with muscular dystrophy The Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) has affiliated with Shriners Hospitals for Children Chicago in a clinical partnership to provide care for children with neuromuscular diseases It is caused by mutations in the X-chromosomal DMD gene from which Lattice corneal dystrophy is differentiated among the three major stromal corneal dystrophies (granular, macular, and lattice) based on history and examination. What is the most common autosomal recessive disease? Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is a heritable, bilateral corneal dystrophy characterized by corneal opacification and nystagmus. Showing Results for "autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2i" Filter Results
@article{Mclaughlin1995MutationSO, title={Mutation spectrum of the gene encoding the beta subunit of rod phosphodiesterase among patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. CiteSeerX - Scientific documents that cite the following paper: Abbasi AH, Garzozi HJ, Banin E, BenYosef T. A common founder mutation of CERKL underlies autosomal recessive retinal degeneration with early macular involvement among Yemenite Jews. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene. Autosomal Recessive inheritance. Macular corneal dystrophy (MCD) is a rare, severe form of stromal corneal dystrophy (see this term) characterized by bilateral ill-defined cloudy regions within a hazy stroma, and eventually severe visual impairment. The hallmark of Schnyder corneal dystrophy is the accumulation of crystals within the corneal stroma which cause corneal clouding typically in a ring-shaped fashion. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED, formerly CHED2) is most likely only an autosomal recessive disorder. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy: Autosomal dominant (maps to 20q12-q13.1) or autosomal recessive Edematous epithelium with lack of Bowman layer Thickened stroma and Descemet membrane Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive condition in which there is abnormality of proteoglycan synthesis. The disorders have some similar characteristics; most forms of corneal dystrophy affect both eyes (bilateral), progress slowly, do not affect other areas of the body, and tend to run in families. Most forms are inherited as autosomal dominant traits; a few are inherited as autosomal recessive traits.
It commonly presents as a
The first step in diagnosing MD is a visit with a healthcare provider for a physical exam This autosomal recessive gene is located on the X chromosome, which is why most of the reported cases have been male Muscular Dystrophy has ten sub-classifications while Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis or ALS has no classes or Those affected by
Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy 2, Autosomal Recessive; CHED2 is a rare disease. The format is GTR00000001.1, with a leading prefix 'GTR' followed by 8 digits, a period, then 1 or more digits representing the version. The format is GTR00000001.1, with a leading prefix 'GTR' followed by 8 digits, a period, then 1 or more digits representing the version. The chromosome locus of Thiel-Behnke corneal dystrophy is only located on 5q31. The entity previously designated as a variant of Thiel-Behnke corneal dystrophy on chromosome 10q24 may represent a novel corneal dystrophy. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED, formerly CHED2) is most likely only an autosomal recessive disorder. It usually presents in the first two decades of life with subepithelial nodular lesions that later coalesce to form mulberry-like opacities.
Search: Muscular Dystrophy Lifespan. Treatment No Feedback. METHODS. The onset of corneal haze is variable. Check the full list of possible causes and conditions now! Macular corneal dystrophy is the only autosomal recessive corneal stromal dystrophy and also the only dystrophy that can extend out to the limbus. Explore symptoms, inheritance, genetics of this condition. The gene for autosomal dominant congenital hereditary endothelial corneal dystrophy has not been identified, but it is located on the short arm of chromosome 20 (20p11.2-q11.20). The present disclosure provides methods for treating autosomal dominant diseases in a subject. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness (CDPD) is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the SLC4A11 gene ( 610206 ), which encodes a sodium borate cotransporter, on chromosome 20p13. Posterior corneal dystrophies Fuchs corneal dystrophy presents during the fifth or sixth decade of life.
Objectives: To report a child with early-onset autosomal recessive Best vitelliform macular dystrophy and compound heterozygous BEST1 mutations, the management of a choroidal neovascular membrane with intravitreal bevacizumab in the proband, the benefits of amblyopia therapy in the fellow eye, and the findings in the parents, carriers of heterozygous BEST1 Hearing deficit in CDPD is slowly progressive and is typically Spinocerebellar ataxia ( SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, [1] genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. RP is inherited either in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X-linked mode. Different immunophenotypes have been described depending on the presence of keratan sulfate in cornea and/or serum.
Autosomal recessive is a pattern of inheritance characteristic of some genetic disorders. CHED can be divided into 2 types by the modes of inheritance; CHED type 1 (CHED1) with autosomal dominant inheritance and CHED type 2 (CHED2) with autosomal recessive inheritance. Allelic and locus heterogeneity in autosomal recessive gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy. Contribute to andreioradu/adaptic-files development by creating an account on GitHub. As shown in the figure, to have symptoms of Bietti's Crystalline Dystrophy (BCD), an individual must have two copies of the same disease gene. The Slc4a11 KO mouse model was generated by gene deletion. Autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy, also called congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2, MIM 217700), is an uncommon hereditary corneal disorder clinically presenting at birth or in early childhood. It is relatively common in Japan. The autosomal recessive form of congenital hereditary endothelial corneal dystrophy is due to mutations in the SLC4A11 gene on chromosome 20(20p13).
Autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy (CHED2) is associated with mutations in SLC4A11. Muscle-Eye-Brain disease (MEB) and Fukuyama type congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD) are clinically similar autosomal recessive diseases, characterized by congenital muscular dystrophy and Macular corneal dystrophy, 217800, Autosomal recessive; MCD (Macular corneal dystrophy) (CHST6 gene) (Sequence Analysis-All Coding Exons) (Postnatal) GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific, orderable test from a particular laboratory, and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Recessive means that two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) are required to cause the disorder. Macular corneal dystrophy is an autosomal recessive condition in which there is abnormality of proteoglycan synthesis. We report on a patient with autosomal recessive cutis laxa type IIIA, due to a homozygous missense c.1273C > T; p. Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of the corneal endothelium characterized by nonprogressive bilateral corneal edema Autosomal recessive corneal amyloidosis results from multiple mutations in the M1S1 (TACSTD2) gene located on chromosome 1 (1p32). Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and cone-rod dystrophy caused by splice site mutations in the Stargardts disease gene ABCR. Macular dystrophy, corneal type 1 is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly. X. Jiao, A. Sultana, +5 authors C A family has three siblings suffering from congenital corneal dystrophy in association with progressive sensorineural deafness, and all the positive findings in these patients are attributed to a single gene. It is characterized by multiple irregular gray-white opacities in the corneal stroma that extend out into the peripheral cornea and down to the Descemet membrane. List of variants reported as not provided for Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A2; Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with intellectual disability), type B2; Autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2N